Targeting the host response in sepsis: current approaches and future evidence
- PMID: 38057824
- PMCID: PMC10698949
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04762-6
Targeting the host response in sepsis: current approaches and future evidence
Abstract
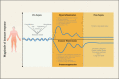
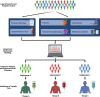
Sepsis, a dysregulated host response to infection characterized by organ failure, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Disbalances of the immune response play an important role in its pathophysiology. Patients may develop simultaneously or concomitantly states of systemic or local hyperinflammation and immunosuppression. Although a variety of effective immunomodulatory treatments are generally available, attempts to inhibit or stimulate the immune system in sepsis have failed so far to improve patients' outcome. The underlying reason is likely multifaceted including failure to identify responders to a specific immune intervention and the complex pathophysiology of organ dysfunction that is not exclusively caused by immunopathology but also includes dysfunction of the coagulation system, parenchymal organs, and the endothelium. Increasing evidence suggests that stratification of the heterogeneous population of septic patients with consideration of their host response might led to treatments that are more effective. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of current studies aimed at optimizing the many facets of host response and to discuss future perspectives for precision medicine approaches in sepsis.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Clinical studies; Disease tolerance; Immunomodulation; Immunosuppression; Immunotherapy; Personalized medicine; Precision medicine; Septic shock.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

