Dasatinib-Induced Transverse Melanonychia
- PMID: 38058546
- PMCID: PMC10697754
- DOI: 10.1159/000531928
Dasatinib-Induced Transverse Melanonychia
Abstract
Introduction: Transverse melanonychia, characterized by grey to black pigmented bands traversing the nail plate, can occur as a side-effect of certain medications. While no documented reports specifically associate dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, with nail changes, we present a case of transverse melanonychia possibly related to dasatinib therapy.
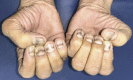
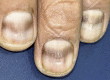
Case report: A 54-year-old male with CML, receiving dasatinib for 1.5 years, presented with transverse pigmented lines involving all fingernails and toenails. Clinical examination revealed discrete bands of transverse melanonychia in the nails. Onychoscopy of all finger- and toenails revealed multiple longitudinal grey lines within transverse grey bands of homogeneous chromonychia. Based on clinical presentation, onychoscopic features, and temporal association with dasatinib therapy, a provisional diagnosis of dasatinib-induced transverse melanonychia was made.
Discussion: The exact mechanisms underlying melanonychia are not fully understood but may involve nail matrix or toxicity, stimulation of nail-matrix melanocytes, or drug deposition within the nail plate. This case highlights the possibility of dasatinib-induced transverse melanonychia and underscores the importance of monitoring and evaluating nail changes in patients undergoing dasatinib treatment.
Keywords: Chemotherapy-induced nail change; Dasatinib; Drug-induced melanonychia; Onychoscopy; Transverse melanonychia.
© 2023 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. None of the authors report any form of support or financial involvement. There are no nonfinancial relationships (personal, political, or professional) that may potentially influence the writing of the manuscript.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

