Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug formulated with anthraflavic acid for treating human breast carcinoma and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38058699
- PMCID: PMC10696992
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms/141173
Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug formulated with anthraflavic acid for treating human breast carcinoma and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
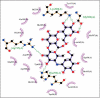
Introduction: Molecular docking as a versatile theoretical method was used to investigate the biological activities of anthraflavic acid in the presence of α-amylase. The outcomes revealed that anthraflavic acid has a considerable binding affinity to the enzyme with a docking score of -7.913 kcal/mol. These outcomes were further evaluated with free binding energy calculations, and it was concluded that anthraflavic acid could be a potential inhibitor for α-amylase.
Material and methods: Anthraflavic acid was explored in anti-human breast carcinoma tests. The in vitro cytotoxic and anti-breast carcinoma effects of biologically synthesized anthraflavic acid against MCF-7, CAMA-1, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, AU565 [AU-565], and Hs 281.T cancer cell lines were assessed. In the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, the anti-breast carcinoma properties of anthraflavic acid could significantly kill the MCF-7, CAMA-1, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, AU565 [AU-565], and Hs 281.T cancer cell lines in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Also, we used human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to determine the cytotoxicity potentials of anthraflavic acid using MTT assay.
Results: The IC50 values of anthraflavic acid were 159, 193, 253, 156, 241, and 218 μg/ml against MCF-7, CAMA-1, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, AU565 [AU-565], and Hs 281.T cancer cell lines.
Conclusions: It seems the anti-human breast carcinoma effect of recent nanoparticles is due to their antioxidant effects.
Keywords: anthraflavic acid; cytotoxic; human breast carcinoma; molecular docking; α-amylase.
Copyright: © 2021 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Brown JP. A review of the genetic effects of naturally occurring flavonoids, anthraquinolines and related compounds. Mutation Res 1980; 75: 243-77. - PubMed
-
- Turesky RJ, Skipper DL, Tannenbaum SR, Coles B, Ketterer B. Sulfamate formation is a major route for detoxification of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in the rat. Carcinogenesis 1986; 7: 1483-5. - PubMed
-
- Sayer JM, Yagi H, Wood AW, Conney AH, Jerina DM. Extreme facile reaction between the ultimate carcinogen benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide and ellagic acid. J Am Chem Soc 1982; 104: 5562-4.
-
- Koçyiğit ÜM, Taslimi P, Tüzün B, Yakan H, Muğlu H, Güzel E. 1,2,3-Triazole substituted phthalocyanine metal complexes as potential inhibitors for anticholinesterase and antidiabetic enzymes with molecular docking studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2022; 40: 4429-39. - PubMed
-
- Jhong CH, Riyaphan J, Lin SH, Chia YC, Weng CF. Screening alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase inhibitors from natural compounds by molecular docking in silico. BioFactors 2015; 41: 242-51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
