Endothelin System in Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38059359
- PMCID: PMC10954415
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21716
Endothelin System in Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
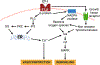
ET (endothelin) is a powerful vasoconstrictor 21-amino acid peptide present in many tissues, which exerts many physiological functions across the body and participates as a mediator in many pathological conditions. ETs exert their effects through ETA and ETB receptors, which can be blocked by selective receptor antagonists. ETs were shown to play important roles among others, in systemic hypertension, particularly when resistant or difficult to control, and in pulmonary hypertension, atherosclerosis, cardiac hypertrophy, subarachnoid hemorrhage, chronic kidney disease, diabetic cardiovascular disease, scleroderma, some cancers, etc. To date, ET antagonists are only approved for the treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension and recently for IgA nephropathy and used in the treatment of digital ulcers in scleroderma. However, they may soon be approved for the treatment of patients with resistant hypertension and different types of nephropathy. Here, the role of ETs is reviewed with a special emphasis on participation in and treatment of hypertension and chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathies; endothelin receptor antagonists; glomerulosclerosis, focal segmental; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
E.L. Schiffrin has participated in advisory boards of Janssen Pharmaceuticals, USA. The other author reports no conflicts.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

