Comparative evaluation of small molecules reported to be inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation
- PMID: 38059629
- PMCID: PMC10782960
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03147-23
Comparative evaluation of small molecules reported to be inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation
Abstract
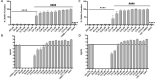
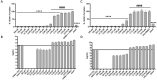
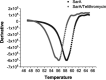
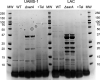
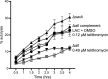
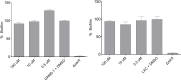
Because biofilm formation is such a problematic feature of Staphylococcus aureus infections, much effort has been put into identifying biofilm inhibitors. However, the results observed with these compounds are often reported in isolation, and the methods used to assess biofilm formation vary between labs, making it impossible to assess relative efficacy and prioritize among these putative inhibitors for further study. The studies we report address this issue by directly comparing putative biofilm inhibitors using a consistent in vitro assay. This assay was previously shown to maximize biofilm formation, and the results observed with this assay have been proven to be relevant in vivo. Of the 19 compounds compared using this method, many had no impact on biofilm formation under these conditions. Indeed, only one proved effective at limiting biofilm formation without also inhibiting growth.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance; antimicrobial activity; antimicrobial agents; biofilms; infectious disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
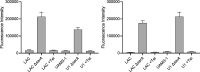
Similar articles
-
Promising treatment strategies to combat Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infections: an updated review.Biofouling. 2020 Nov;36(10):1159-1181. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2020.1857743. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Biofouling. 2020. PMID: 33353409 Review.
-
Susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in diabetic foot infections.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jun 23;16(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0737-0. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27339028 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules Produced by Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis Disrupt Formation of Biofilms by Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18;86(5):e02539-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02539-19. Print 2020 Feb 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31862721 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Staphylococcus aureus amidase catalytic domain inhibitor to prevent biofilm formation by sequential virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation and biological evaluation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 2):127842. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127842. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37924909
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
Cited by
-
Increased production of aureolysin and staphopain A is a primary determinant of the reduced virulence of Staphylococcus aureus sarA mutants in osteomyelitis.mBio. 2024 Apr 10;15(4):e0338323. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03383-23. Epub 2024 Feb 28. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38415646 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm-Associated Infections: Have We Found a Clinically Relevant Target?Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 9;13(4):852. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040852. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pompilio A, Scocchi M, Mangoni ML, Shirooie S, Serio A, Ferreira Garcia da Costa Y, Alves MS, Şeker Karatoprak G, Süntar I, Khan H, Di Bonaventura G. 2023. Bioactive compounds: a goldmine for defining new strategies against pathogenic bacterial biofilms? Crit Rev Microbiol 49:117–149. doi:10.1080/1040841X.2022.2038082 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

