Targeting dysregulated lipid metabolism in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 38060103
- PMCID: PMC10725365
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-023-01473-y
Targeting dysregulated lipid metabolism in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
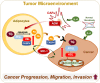
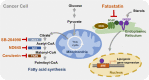
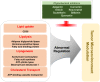
The reprogramming of lipid metabolism and its association with oncogenic signaling pathways within the tumor microenvironment (TME) have emerged as significant hallmarks of cancer. Lipid metabolism is defined as a complex set of molecular processes including lipid uptake, synthesis, transport, and degradation. The dysregulation of lipid metabolism is affected by enzymes and signaling molecules directly or indirectly involved in the lipid metabolic process. Regulation of lipid metabolizing enzymes has been shown to modulate cancer development and to avoid resistance to anticancer drugs in tumors and the TME. Because of this, understanding the metabolic reprogramming associated with oncogenic progression is important to develop strategies for cancer treatment. Recent advances provide insight into fundamental mechanisms and the connections between altered lipid metabolism and tumorigenesis. In this review, we explore alterations to lipid metabolism and the pivotal factors driving lipid metabolic reprogramming, which exacerbate cancer progression. We also shed light on the latest insights and current therapeutic approaches based on small molecular inhibitors and phytochemicals targeting lipid metabolism for cancer treatment. Further investigations are worthwhile to fully understand the underlying mechanisms and the correlation between altered lipid metabolism and carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Cholesterol transport; Lipid uptake; Lipogenesis; Lipolysis; Phytochemical; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abumrad NA, El-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, Grimaldi PA. Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:17665–17668. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)46753-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aguirre-Portoles C, Feliu J, Reglero G, Ramirez de Molina A. ABCA1 overexpression worsens colorectal cancer prognosis by facilitating tumour growth and caveolin-1-dependent invasiveness, and these effects can be ameliorated using the BET inhibitor apabetalone. Mol Oncol. 2018;12:1735–1752. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12367. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

