Shared and distinct pathways and networks genetically linked to coronary artery disease between human and mouse
- PMID: 38060277
- PMCID: PMC10703441
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.88266
Shared and distinct pathways and networks genetically linked to coronary artery disease between human and mouse
Abstract
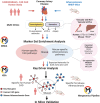
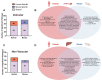
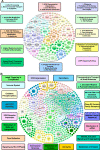
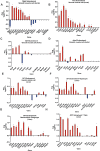
Mouse models have been used extensively to study human coronary artery disease (CAD) or atherosclerosis and to test therapeutic targets. However, whether mouse and human share similar genetic factors and pathogenic mechanisms of atherosclerosis has not been thoroughly investigated in a data-driven manner. We conducted a cross-species comparison study to better understand atherosclerosis pathogenesis between species by leveraging multiomics data. Specifically, we compared genetically driven and thus CAD-causal gene networks and pathways, by using human GWAS of CAD from the CARDIoGRAMplusC4D consortium and mouse GWAS of atherosclerosis from the Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP) followed by integration with functional multiomics human (STARNET and GTEx) and mouse (HMDP) databases. We found that mouse and human shared >75% of CAD causal pathways. Based on network topology, we then predicted key regulatory genes for both the shared pathways and species-specific pathways, which were further validated through the use of single cell data and the latest CAD GWAS. In sum, our results should serve as a much-needed guidance for which human CAD-causal pathways can or cannot be further evaluated for novel CAD therapies using mouse models.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; computational biology; coronary artery disease; cross-species comparison; gene regulatory networks; human; mouse; multiomics; systems biology.
© 2023, Kurt, Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ZK, JC, RB, CM, ZS, NH, NJ, CP, OF, SK, SW, JB, AL, MB, XY No competing interests declared
Figures

Update of
-
Shared and distinct pathways and networks genetically linked to coronary artery disease between human and mouse.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 20:2023.06.08.544148. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.08.544148. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Dec 07;12:RP88266. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88266. PMID: 37333408 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
From mouse to human.Elife. 2023 Dec 7;12:e94382. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94382. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38060304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alpaydin E. Introduction to Machine Learning Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning. The MIT Press; 2010.
-
- Aragam KG, Jiang T, Goel A, Kanoni S, Wolford BN, Atri DS, Weeks EM, Wang M, Hindy G, Zhou W, Grace C, Roselli C, Marston NA, Kamanu FK, Surakka I, Venegas LM, Sherliker P, Koyama S, Ishigaki K, Åsvold BO, Brown MR, Brumpton B, de Vries PS, Giannakopoulou O, Giardoglou P, Gudbjartsson DF, Güldener U, Haider SMI, Helgadottir A, Ibrahim M, Kastrati A, Kessler T, Kyriakou T, Konopka T, Li L, Ma L, Meitinger T, Mucha S, Munz M, Murgia F, Nielsen JB, Nöthen MM, Pang S, Reinberger T, Schnitzler G, Smedley D, Thorleifsson G, von Scheidt M, Ulirsch JC, Biobank Japan. EPIC-CVD. Arnar DO, Burtt NP, Costanzo MC, Flannick J, Ito K, Jang D-K, Kamatani Y, Khera AV, Komuro I, Kullo IJ, Lotta LA, Nelson CP, Roberts R, Thorgeirsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Webb TR, Baras A, Björkegren JLM, Boerwinkle E, Dedoussis G, Holm H, Hveem K, Melander O, Morrison AC, Orho-Melander M, Rallidis LS, Ruusalepp A, Sabatine MS, Stefansson K, Zalloua P, Ellinor PT, Farrall M, Danesh J, Ruff CT, Finucane HK, Hopewell JC, Clarke R, Gupta RM, Erdmann J, Samani NJ, Schunkert H, Watkins H, Willer CJ, Deloukas P, Kathiresan S, Butterworth AS, CARDIoGRAMplusC4D Consortium Discovery and systematic characterization of risk variants and genes for coronary artery disease in over a million participants. Nature Genetics. 2022;54:1803–1815. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01233-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. 1995;57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x. - DOI
-
- Bennett BJ, Farber CR, Orozco L, Kang HM, Ghazalpour A, Siemers N, Neubauer M, Neuhaus I, Yordanova R, Guan B, Truong A, Yang W, He A, Kayne P, Gargalovic P, Kirchgessner T, Pan C, Castellani LW, Kostem E, Furlotte N, Drake TA, Eskin E, Lusis AJ. A high-resolution association mapping panel for the dissection of complex traits in mice. Genome Research. 2010;20:281–290. doi: 10.1101/gr.099234.109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01HL168174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117850/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL168174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148239/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL164577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL164577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147883/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148239/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL166428/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL166428/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

