Safety and Efficacy of Biologic Therapies (Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab) in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38060699
- PMCID: PMC10698389
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.48338
Safety and Efficacy of Biologic Therapies (Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab) in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A Systematic Review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Safety and Efficacy of Biologic Therapies (Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab) in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Sep 24;17(9):c318. doi: 10.7759/cureus.c318. eCollection 2025 Sep. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 41000146 Free PMC article.
Abstract
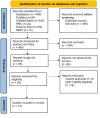
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic disorders, including Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), that contribute to inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, manifesting as bloody diarrhea, fecal urgency, bloating, cramping, and weight loss. IBD manifests as an exacerbation of these symptoms, which medications with high side effect profiles can manage; consequently, many novel therapies, including biologics such as ustekinumab and vedolizumab, have been developed over the years. This systematic review aims to assess the safety and efficacy of ustekinumab and vedolizumab in treating inflammatory bowel disease based on a comprehensive analysis of relevant studies. A thorough literature search was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials, post hoc analyses, case reports, observational cohorts, and meta-analyses involving ustekinumab and vedolizumab as treatment in IBD patients. The selected studies were critically evaluated for their methodology, patient characteristics, and outcomes. The analysis involved twelve distinct studies investigating the impact of ustekinumab and vedolizumab on individuals afflicted with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The findings revealed a notable trend: ustekinumab displayed a propensity for yielding higher rates of clinical remission in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). Moreover, one study underscored substantial reductions in endoscopic disease activity in patients with Crohn's disease (CD) who were on ustekinumab. Similarly, ustekinumab exhibited promising outcomes in CD patients, including swift ultrasound responses and the achievement of transmural remission, particularly among those who were new to biologic treatments. In line with this, vedolizumab demonstrated early and considerable symptomatic improvements when used to treat both UC and CD patients. While both biologics showed promising results in inducing and maintaining remission, cautious monitoring is warranted due to the potential adverse events observed in some cases. Further research with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up periods is needed to establish a comprehensive understanding of the medications' effects on IBD patients.
Keywords: ibd; remission; treatment; ustekinumab; vedolizumab.
Copyright © 2023, Ashraf et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Crohn's disease. Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. The Lancet. 2012;9853:1590–1605. - PubMed
-
- The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025. Kaplan GG. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12:720–727. - PubMed
-
- A real-world, long-term experience on effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the Cross Pennine study. Lenti MV, Levison S, Eliadou E, et al. Dig Liver Dis. 2018;50:1299–1304. - PubMed
-
- Vedolizumab, a humanised mAb against the α4β7 integrin for the potential treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Tilg H, Kaser A. https://europepmc.org/article/med/21157649 Curr Opin Investig. 2010;11:1295–1304. - PubMed
-
- Dual biologic or small molecule therapy for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ahmed W, Galati J, Kumar A, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:0–79. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources