Cationic Porphyrin-Based Ionic Nanomedicines for Improved Photodynamic Therapy
- PMID: 38063308
- PMCID: PMC10777306
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00809
Cationic Porphyrin-Based Ionic Nanomedicines for Improved Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
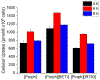
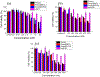
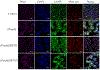
This study presents the synthesis and characterization of monosubstituted cationic porphyrin as a photodynamic therapeutic agent. Cationic porphyrin was converted into ionic materials by using a single-step ion exchange reaction. The small iodide counteranion was replaced with bulky BETI and IR783 anions to reduce aggregation and enhance the photodynamic effect of porphyrin. Carrier-free ionic nanomedicines were then prepared by using the reprecipitation method. The photophysical characterization of parent porphyrin, ionic materials, and ionic nanomaterials, including absorbance, fluorescence and phosphorescence emission, quantum yield, radiative and nonradiative rate, and lifetimes, was performed. The results revealed that the counteranion significantly affects the photophysical properties of porphyrin. The ionic nanomaterials exhibited an increase in the reactive oxygen yield and enhanced cytotoxicity toward the MCF-7 cancer cell line. Examination of results revealed that the ionic materials exhibited an enhanced photodynamic therapeutic activity with a low IC50 value (nanomolar) in cancerous cells. These nanomedicines were mainly localized in the mitochondria. The improved light cytotoxicity is attributed to the enhanced photophysical properties and positive surface charge of the ionic nanomedicines that facilitate efficient cellular uptake. These results demonstrate that ionic material-based nanodrugs are promising photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy.
Keywords: cancer therapy; cytotoxicity; ionic materials; nanoparticles; organic synthesis; singlet oxygen; subcellular localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



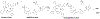
References
-
- Siegel RL; Miller KD; Sauer AG; Fedewa SA; Butterly LF; Anderson JC; Cercek A; Smith RA; Jemal A Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2020. Ca-Cancer J. Clin 2020, 70 (3), 145–164. - PubMed
-
- Partridge AH; Burstein HJ; Winer EP Side Effects of Chemotherapy and Combined Chemohormonal Therapy in Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr 2001, 02115 (30), 135–142. - PubMed
-
- Ethirajan M; Chen Y; Joshi P; Pandey RK The Role of Porphyrin Chemistry in Tumor Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40 (1), 340–362. - PubMed
-
- Siraj N; Kolic PE; Regmi BP; Warner IM Strategy for Tuning the Photophysical Properties of Photosensitizers for Use in Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. - Eur. J 2015, 21 (41), 14440–14446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
