A Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing for Prescribing High-Intensity Interval Training Sessions with Elastic Resistance
- PMID: 38063527
- PMCID: PMC10706320
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20237097
A Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing for Prescribing High-Intensity Interval Training Sessions with Elastic Resistance
Abstract
This study aims to analyze the agreement of cardiopulmonary variables between a cardiopulmonary exercise test with elastic resistance (CPxEL) and high-intensity interval exercise with elastic resistance (EL-HIIE).
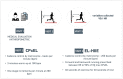
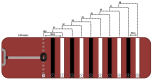
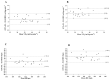
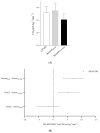
Methods: Twenty-two physically independent participants were recruited. Visit one consisted of conducting a health survey and anthropometric assessment. On visit two, the participants performed CPxEL. After seven days, on visit three, the participants performed EL-HIIE. The CPxEL was carried out on a rubber mat demarcated by lines representing eight stages. The test consisted of alternating back and forth steps against elastic resistance. The increments were performed at a rate of one stage per minute, following a cadence controlled by a metronome calibrated by beats per minute (bpm). The EL-HIIE was performed at the stage corresponding to an intensity of ~85% VO2max, as determined by CPxEL. The EL-HIIE consisted of 10 × 1 min (work):1 min (passive rest), with a cadence of 200 bpm. Cardiopulmonary parameters, heart rate (HR), and oxygen consumption (VO2) were measured during exercise. Bland-Altman was applied to analyze the agreement between the HR and VO2 found in EL-HIIE and the values prescribed by CPxEL (~85-90% VO2max).
Results: The HRpeak and VO2peak in the EL-HIIE showed good agreement with the VO2CPxEL and HRCPxEL values, showing an average difference of (-1.7 mL·kg-1·min-1) and (0.3 bpm).
Conclusions: The results of the present study demonstrate the agreement of cardiopulmonary variables between the CPxEL and the EL-HIIE. Therefore, for a more specific prescription of EL-HIIE intensity, CPxEL can be used.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary exercise testing; high-intensity interval training; oxygen consumption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

