Ti3C2-MXene/NiO Nanocomposites-Decorated CsPbI3 Perovskite Active Materials under UV-Light Irradiation for the Enhancement of Crystal-Violet Dye Photodegradation
- PMID: 38063722
- PMCID: PMC10707859
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13233026
Ti3C2-MXene/NiO Nanocomposites-Decorated CsPbI3 Perovskite Active Materials under UV-Light Irradiation for the Enhancement of Crystal-Violet Dye Photodegradation
Abstract
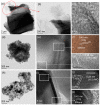
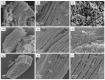
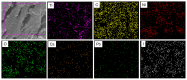
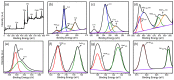
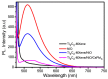
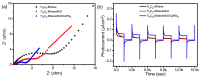
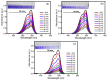
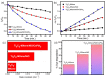
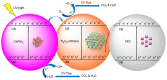
Ti3C2-MXene material, known for its strong electronic conductivity and optical properties, has emerged as a promising alternative to noble metals as a cocatalyst for the development of efficient photocatalysts used in environmental cleanup. In this study, we investigated the photodegradation of crystal-violet (CV) dye when exposed to UV light using a newly developed photocatalyst known as Ti3C2-MXene/NiO nanocomposite-decorated CsPbI3 perovskite, which was synthesized through a hydrothermal method. Our research investigation into the structural, morphological, and optical characteristics of the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite using techniques such as FTIR, XRD, TEM, SEM-EDS mapping, XPS, UV-Vis, and PL spectroscopy. The photocatalytic efficacy of the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite was assessed by evaluating its ability to degrade CV dye in an aqueous solution under UV-light irradiation. Remarkably, the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite displayed a significant improvement in both the degradation rate and stability of CV dye when compared to the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO nanocomposite and CsPbI3 perovskite materials. Furthermore, the UV-visible absorption spectrum of the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite demonstrated a reduced band gap of 2.41 eV, which is lower than that of Ti3C2-MXene/NiO (3.10 eV) and Ti3C2-MXene (1.60 eV). In practical terms, the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite achieved an impressive 92.8% degradation of CV dye within 90 min of UV light exposure. We also confirmed the significant role of photogenerated holes and radicals in the CV dye removal process through radical scavenger trapping experiments. Based on our findings, we proposed a plausible photocatalytic mechanism for the Ti3C2-MXene/NiO/CsPbI3 composite. This research may open up new avenues for the development of cost-effective and high-performance MXene-based perovskite photocatalysts, utilizing abundant and sustainable materials for environmental remediation.
Keywords: NiO; Ti3C2-MXene; UV-light irradiation; crystal violet; perovskite; photodegradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synthesis and characterization of NiO/Cr2O3 nanocomposite with effective sunlight driven photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jun;30(28):71957-71969. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-22746-x. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36040696
-
Ag3PO4-Deposited TiO2@Ti3C2 Petals for Highly Efficient Photodecomposition of Various Organic Dyes under Solar Light.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;12(14):2464. doi: 10.3390/nano12142464. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889687 Free PMC article.
-
0D/2D Heterojunctions of Ti3C2 MXene QDs/SiC as an Efficient and Robust Photocatalyst for Boosting the Visible Photocatalytic NO Pollutant Removal Ability.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Sep 9;12(36):40176-40185. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c01013. Epub 2020 Aug 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32803949
-
Environmental remediation of hazardous pollutants using MXene-perovskite-based photocatalysts: A review.Environ Res. 2023 Oct 1;234:116576. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116576. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37423362 Review.
-
Ti3C2Tx MXene-Based Hybrid Photocatalysts in Organic Dye Degradation: A Review.Molecules. 2025 Mar 26;30(7):1463. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071463. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitivity-Enhanced, Room-Temperature Detection of NH3 with Alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Apr 15;14(8):680. doi: 10.3390/nano14080680. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668174 Free PMC article.
-
All-inorganic lead halide perovskites for photocatalysis: a review.RSC Adv. 2024 Feb 7;14(7):4946-4965. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07998h. eCollection 2024 Jan 31. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38327811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interface Engineering, Charge Carrier Dynamics, and Solar-Driven Applications of Halide Perovskite/2D Material Heterostructured Photocatalysts.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Apr 23;17(16):23431-23465. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c20972. Epub 2025 Apr 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40211476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chu E.W., Karr J.R. Reference Module in Life Sciences. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. Environmental Impact: Concept, Consequences, Measurement; pp. 1–22. - DOI
-
- Akinnawo S.O. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, Physical, Chemical and Biological Techniques for Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Chall. 2023;12:100733. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2023.100733. - DOI
-
- Shabir M., Yasin M., Hussain M., Shafiq I., Akhter P., Nizami A.S., Jeon B.H., Park Y.K. A Review on Recent Advances in the Treatment of Dye-Polluted Wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022;112:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2022.05.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

