17q21 Variants Disturb Mucosal Host Defense in Childhood Asthma
- PMID: 38064241
- PMCID: PMC11531215
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202305-0934OC
17q21 Variants Disturb Mucosal Host Defense in Childhood Asthma
Erratum in
-
Erratum: 17q21 Variants Disturb Mucosal Host Defense in Childhood Asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Jun 15;209(12):1519. doi: 10.1164/rccm.v209erratum9. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38874229 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Erratum: Missing Funder in "17q21 Variants Disturb Mucosal Host Defense in Childhood Asthma".Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Sep 1;210(5):697-698. doi: 10.1164/rccm.v210erratum3. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39212341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
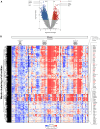
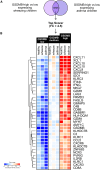
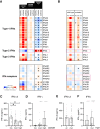
Rationale: The strongest genetic risk factor for childhood-onset asthma, the 17q21 locus, is associated with increased viral susceptibility and disease-promoting processes.Objectives: To identify biological targets underlying the escalated viral susceptibility associated with the clinical phenotype mediated by the 17q21 locus.Methods: Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of nasal brush samples from 261 children (78 healthy, 79 with wheezing at preschool age, 104 asthmatic) within the ALLIANCE (All-Age-Asthma) cohort, with a median age of 10.0 (range, 1.0-20.0) years, was conducted to explore the impact of their 17q21 genotype (SNP rs72163891). Concurrently, nasal secretions from the same patients and visits were collected, and high-sensitivity mesoscale technology was employed to measure IFN protein levels.Measurements and Main Results: This study revealed that the 17q21 risk allele induces a genotype- and asthma/wheeze phenotype-dependent enhancement of mucosal GSDMB expression as the only relevant 17q21-encoded gene in children with preschool wheeze. Increased GSDMB expression correlated with the activation of a type-1 proinflammatory, cell-lytic immune, and natural killer signature, encompassing key genes linked to an IFN type-2-signature (IFNG, CXCL9, CXCL10, KLRC1, CD8A, GZMA). Conversely, there was a reduction in IFN type 1 and type 3 expression signatures at the mRNA and protein levels.Conclusions: This study demonstrates a novel disease-driving mechanism induced by the 17q21 risk allele. Increased mucosal GSDMB expression is associated with a cell-lytic immune response coupled with compromised airway immunocompetence. These findings suggest that GSDMB-related airway cell death and perturbations in the mucosal IFN signature account for the increased vulnerability of 17q21 risk allele carriers to respiratory viral infections during early life, opening new options for future biological interventions.The All-Age-Asthma (ALLIANCE) cohort is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov (pediatric arm, NCT02496468).
Keywords: ALLIANCE; asthma; nasal transcriptome; preschool wheeze.
Figures

Comment in
-
Novel Role of the GSDMB/IFNG Axis in Childhood Asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Apr 15;209(8):899-900. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202312-2259ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38300150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moffatt MF, Kabesch M, Liang L, Dixon AL, Strachan D, Heath S, et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature . 2007;448:470–473. - PubMed
-
- Ober C, McKennan CG, Magnaye KM, Altman MC, Washington C, III, Stanhope C, et al. Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes-Children’s Respiratory Research Workgroup Expression quantitative trait locus fine mapping of the 17q12-21 asthma locus in African American children: a genetic association and gene expression study. Lancet Respir Med . 2020;8:482–492. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouzigon E, Corda E, Aschard H, Dizier MH, Boland A, Bousquet J, et al. Effect of 17q21 variants and smoking exposure in early-onset asthma. N Engl J Med . 2008;359:1985–1994. - PubMed
-
- Gorlanova O, Illi S, Toncheva AA, Usemann J, Latzin P, Kabesch M, et al. BILD and PASTURE study groups Protective effects of breastfeeding on respiratory symptoms in infants with 17q21 asthma risk variants. Allergy . 2018;73:2388–2392. - PubMed
-
- Ege MJ, Mayer M, Normand AC, Genuneit J, Cookson WO, Braun-Fahrländer C, et al. GABRIELA Transregio 22 Study Group Exposure to environmental microorganisms and childhood asthma. N Engl J Med . 2011;364:701–709. - PubMed

