Learning-based keypoint registration for fetoscopic mosaicking
- PMID: 38066354
- PMCID: PMC10881678
- DOI: 10.1007/s11548-023-03025-7
Learning-based keypoint registration for fetoscopic mosaicking
Abstract
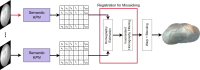
Purpose: In twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), abnormal vascular anastomoses in the monochorionic placenta can produce uneven blood flow between the two fetuses. In the current practice, TTTS is treated surgically by closing abnormal anastomoses using laser ablation. This surgery is minimally invasive and relies on fetoscopy. Limited field of view makes anastomosis identification a challenging task for the surgeon.
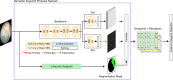
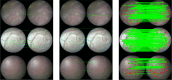
Methods: To tackle this challenge, we propose a learning-based framework for in vivo fetoscopy frame registration for field-of-view expansion. The novelties of this framework rely on a learning-based keypoint proposal network and an encoding strategy to filter (i) irrelevant keypoints based on fetoscopic semantic image segmentation and (ii) inconsistent homographies.
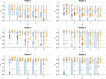
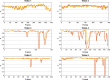
Results: We validate our framework on a dataset of six intraoperative sequences from six TTTS surgeries from six different women against the most recent state-of-the-art algorithm, which relies on the segmentation of placenta vessels.
Conclusion: The proposed framework achieves higher performance compared to the state of the art, paving the way for robust mosaicking to provide surgeons with context awareness during TTTS surgery.
Keywords: Deep learning; Fetal surgery; Fetoscopy; Mosaicking; Self-supervised; Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subjects of this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Baschat A, Chmait RH, Deprest J, Gratacós E, Hecher K, Kontopoulos E, Quintero R, Skupski DW, Valsky DV, Ville Y. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) J Perinat Med. 2011;39(2):107–112. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

