How to manage hemostasis in patients with liver disease during interventions
- PMID: 38066857
- PMCID: PMC10727050
- DOI: 10.1182/hematology.2023000480
How to manage hemostasis in patients with liver disease during interventions
Abstract
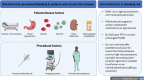
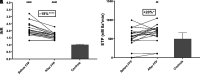
Patients with advanced chronic liver disease (CLD) often need procedures to both treat and prevent complications of portal hypertension such as ascites or gastrointestinal bleeding. Abnormal results for hemostatic tests, such as prolonged prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and/or thrombocytopenia, are commonly encountered, raising concerns about increased bleeding risk and leading to transfusion to attempt to correct prior to interventions. However hemostatic markers are poor predictors of bleeding risk in CLD, and routine correction, particularly with fresh frozen plasma and routine platelet transfusions, should be avoided. This narrative review discusses the hemostatic management of patients with CLD using 2 case descriptions.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Lara N. Roberts: no competing financial interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Northup PG, Garcia-Pagan JC, Garcia-Tsao G, et al.. Vascular liver disorders, portal vein thrombosis, and procedural bleeding in patients with liver disease: 2020 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2021;73(1):366-413. doi:10.1002/hep.31646. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

