Dietary Curcumin Modulating Effect on Performance, Antioxidant Status, and Immune-Related Response of Broiler Chickens Exposed to Imidacloprid Insecticide
- PMID: 38067001
- PMCID: PMC10705146
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13233650
Dietary Curcumin Modulating Effect on Performance, Antioxidant Status, and Immune-Related Response of Broiler Chickens Exposed to Imidacloprid Insecticide
Abstract
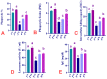
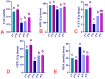
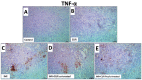
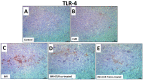
Birds appear to be especially vulnerable to adverse impacts from insecticides. This is especially true for imidacloprid (IMI), which is considered the most toxic to avian species. Recently, prospective studies aimed at including natural alternative products to alleviate the toxic impact that comes from insecticides have been increased. Focusing on herbal growth promoters and antioxidative medicament for the poultry industry, this ongoing experiment was conducted to examine the curcumin role (CUR) in mitigating IMI-prompted detrimental effects on broilers' performance, immunity, and antioxidant status. A total number of one hundred and fifty commercial meat-type Ross 308 broilers chicks (one-day-old) were randomly allocated into equal five groups (30 chicks/group and 10 birds/replicate). The first group (C) was the control; the second group (CUR) was fed a diet containing CUR at the level of 450 mg/kg; the third group (IMI) was fed control diet for 14 days and then was fed a diet containing IMI at the level of 50 mg/kg; the fourth group (CUR+IMI co-treated) was fed a diet containing CUR+IMI; and the fifth group (CUR+IMI pro/co-treated) was fed a diet containing CUR for 14 days as protective and then a diet containing CUR+IMI for the rest of the trial. CUR supplementation either in the (CUR pro/co-treated) or (CUR co-treated) groups significantly (p < 0.05) improved final body weight and total body weight gain while decreasing the total feed intake and feed conversion ratio when compared to the IMI-exposed and non-treated birds. CUR induced a significant (p < 0.05) enhancement in hematological indices, phagocytosis %, phagocytic index, intracellular killing capacity, total proteins, globulin, liver function enzymes, lysozyme activity, and immunoglobulin-G levels compared to IMI-exposed and non-treated birds. In addition, dietary supplementation of CUR significantly (p < 0.05) modulated oxidative stress-related biomarkers in splenic tissues (total antioxidant capacity, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) and decreased malondialdehyde levels (p < 0.05) when compared to IMI-exposed and non-treated birds. CUR significantly down-regulated mRNA levels expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and TLR4 and up-regulated IL-10 mRNA expression levels in spleens of birds when compared to those exposed to IMI-and non-treated. Finally, our results provided new insight into IMI-induced immuno-toxicity in broiler chickens. Furthermore, for the first time, our study informed that CUR can cause an in vivo protective effect against IMI toxicity, principally as a protective and/or as concurrent supplementation during the exposure to IMI toxicity.
Keywords: 308 Ross Broiler; curcumin; growth performance; hematological indices; imidacloprid; immune-related genes mRNA expression; immune-toxicity; oxidative stress; phagocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abd El-Hack M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., Soliman M.M., Youssef G.B., Taha A.E., Soliman S.M., Ahmed A.E., El-Kott A.F. Alternatives to antibiotics for organic poultry production: Types, modes of action and impacts on bird’s health and production. Poult. Sci. 2022;101:101696. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101696. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abou-Kassem D.E., El-Abasy M.M., Al-Harbi M.S., Abol-Ela S., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., El-Saadony M.T., Abd El-Hack M.E., Ashour E.A. Influences of total sulfur amino acids and photoperiod on growth, carcass traits, blood parameters, meat quality and cecal microbial load of broilers. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022;29:1683–1693. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.10.063. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alagawany M., Elnesr S.S., Farag M.R., El-Naggar K., Taha A.E., Khafaga A.F., Madkour M., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., El-Saadony M.T. Betaine and related compounds: Chemistry, metabolism and role in mitigating heat stress in poultry. J. Therm. Biol. 2022;104:103168. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.103168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Righi F., Pitino R., Manuelian C.L., Simoni M., Quarantelli A., De Marchi M., Tsiplakou E. Plant feed additives as natural alternatives to the use of synthetic antioxidant vitamins on poultry performances, health, and oxidative status: A review of the literature in the last 20 years. Antioxidants. 2021;10:659. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050659. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

