Seroconversion in Galapagos Sea Lions (Zalophus wollebaeki) Confirms the Presence of Canine Distemper Virus in Rookeries of San Cristóbal Island
- PMID: 38067007
- PMCID: PMC10705689
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13233657
Seroconversion in Galapagos Sea Lions (Zalophus wollebaeki) Confirms the Presence of Canine Distemper Virus in Rookeries of San Cristóbal Island
Abstract
Background: The emblematic Galapagos sea lion (GSL-Zalophus wollebaeki) has faced an important population decline over the last four decades. There are multiple environmental and biological factors that might be implied in this decrease. Recently, evidence of various zoonotic infectious diseases that can be potential threats has been reported. Considering that in some islands of the archipelago the risk of transmission of infectious diseases may be promoted by the increasing population of domestic dogs, epidemiological vigilance and search of new pathogens are essential. The canine distemper virus (CDV), one of the viral pathogens that generate the most concern for the agencies responsible for the management and conservation of the Galapagos pinnipeds, was detected in the GSL in 2010. However, there is scarce information about its impact on GSL health and about its epidemiology.
Methods: In this study, 110 GSL serum samples were collected during the summer of 2016 and 2017. All samples were exposed to VERO dog SLAM cells expressing the canine SLAM receptor.
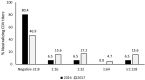
Results: Our results showed a significative increase (p = 0.04) in the frequency of neutralizing antibodies to CDV in the 2017 (53.1%) samples compared to the 2016 samples (19.6%).
Conclusions: Our work confirmed the continuous and increasing circulation of the CDV in the GSL and highlights the importance of monitoring emerging diseases that can be transmitted from domestic to wildlife species. Vigilance of CDV is essential to understand the role of this virus in GSL mortality and to take informed decisions for wildlife conservation.
Keywords: Galapagos Islands; Zalophus wollebaeki; conservation; invasive species; marine mammals; morbillivirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Colón Jaime Grijalva-Rosero passed away in March 2022 prior to the submission of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Trillmich F. Zalophus wollebaeki. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015. [(accessed on 1 November 2023)]. p. e.T41668A45230540. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41668/45230540.
-
- Kalberer S., Meise K., Trillmich F., Krüger O. Reproductive performance of a tropical apex predator in an unpredictable habitat. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018;72:108. doi: 10.1007/s00265-018-2521-7. - DOI
-
- Páez-Rosas D., Guevara N. Tropical Pinnipeds: Bio-Ecology, Threats and Conservation. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: Taylor & Francis Group; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2017. Management strategies and conservation status of Galapagos sea lion populations at San Cristóbal Island, Galapagos, Ecuador; pp. 159–175.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical