Unraveling the Cave: A Seventy-Year Journey into the Caveolar Network, Cellular Signaling, and Human Disease
- PMID: 38067108
- PMCID: PMC10705299
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232680
Unraveling the Cave: A Seventy-Year Journey into the Caveolar Network, Cellular Signaling, and Human Disease
Abstract
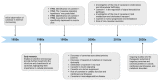
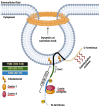
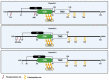
In the mid-1950s, a groundbreaking discovery revealed the fascinating presence of caveolae, referred to as flask-shaped invaginations of the plasma membrane, sparking renewed excitement in the field of cell biology. Caveolae are small, flask-shaped invaginations in the cell membrane that play crucial roles in diverse cellular processes, including endocytosis, lipid homeostasis, and signal transduction. The structural stability and functionality of these specialized membrane microdomains are attributed to the coordinated activity of scaffolding proteins, including caveolins and cavins. While caveolae and caveolins have been long appreciated for their integral roles in cellular physiology, the accumulating scientific evidence throughout the years reaffirms their association with a broad spectrum of human disorders. This review article aims to offer a thorough account of the historical advancements in caveolae research, spanning from their initial discovery to the recognition of caveolin family proteins and their intricate contributions to cellular functions. Furthermore, it will examine the consequences of a dysfunctional caveolar network in the development of human diseases.
Keywords: ECs; calcium signaling; caveolae; caveolin-1; cell senescence; eNOS; endocytosis; lipid rafts; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

