Chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide-Pathological and Physiological Functions in Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 38067112
- PMCID: PMC10705518
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232684
Chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide-Pathological and Physiological Functions in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
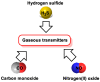
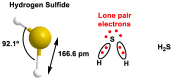
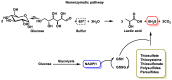
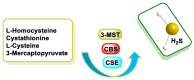
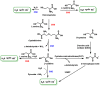
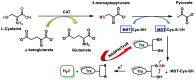
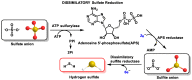
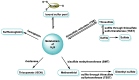
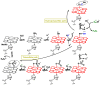
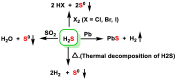
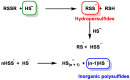
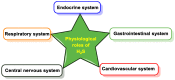
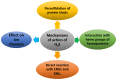
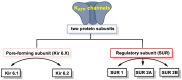
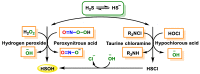
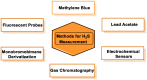
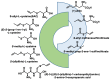
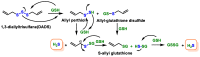
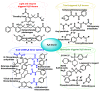
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) was recognized as a gaseous signaling molecule, similar to nitric oxide (-NO) and carbon monoxide (CO). The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the formation of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in the human body. H2S is synthesized by enzymatic processes involving cysteine and several enzymes, including cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS), cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE), cysteine aminotransferase (CAT), 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST) and D-amino acid oxidase (DAO). The physiological and pathological effects of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on various systems in the human body have led to extensive research efforts to develop appropriate methods to deliver H2S under conditions that mimic physiological settings and respond to various stimuli. These functions span a wide spectrum, ranging from effects on the endocrine system and cellular lifespan to protection of liver and kidney function. The exact physiological and hazardous thresholds of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in the human body are currently not well understood and need to be researched in depth. This article provides an overview of the physiological significance of H2S in the human body. It highlights the various sources of H2S production in different situations and examines existing techniques for detecting this gas.
Keywords: chemistry; gasotransmitter; hydrogen sulfide; physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Eduardo Perez Lebeña is an employee of Sistemas de Biotecnología y Recursos Naturales. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
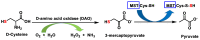
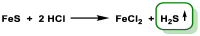

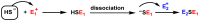
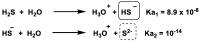

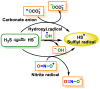

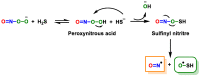
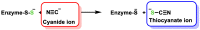
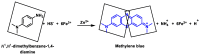
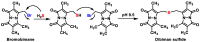
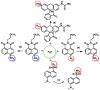
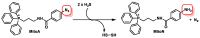
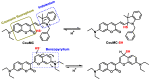
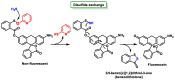
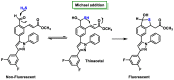
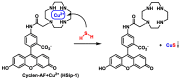
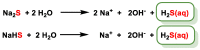
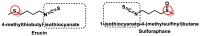
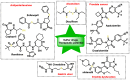
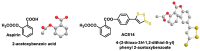
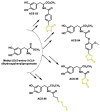
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Project ProID2020010134/Agencia Canaria de Investigación, Innovación y Sociedad de la Información
- 2019SP43/Fundación CajaCanarias
- Grant PID2019-105838RB-C31/Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness
- project PLEC2022-009507/State Plan for Scientific, Technical Research and Innovation 2021-2023 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

