Synergism between IL-33 and MRGPRX2/FcεRI Is Primarily Due to the Complementation of Signaling Modules, and Only Modestly Supplemented by Prolonged Activation of Selected Kinases
- PMID: 38067128
- PMCID: PMC10705352
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232700
Synergism between IL-33 and MRGPRX2/FcεRI Is Primarily Due to the Complementation of Signaling Modules, and Only Modestly Supplemented by Prolonged Activation of Selected Kinases
Abstract
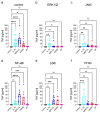
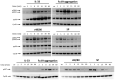
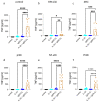
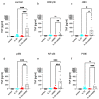
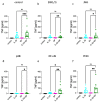
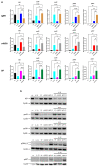
Skin mast cells (MCs) express high levels of MRGPRX2, FcεRI, and ST2, and vigorously respond to their ligands when triggered individually. IL-33/ST2 also potently synergizes with other receptors, but the molecular underpinnings are poorly understood. Human skin-derived MCs were stimulated via different receptors individually or jointly in the presence/absence of selective inhibitors. TNF was quantified by ELISA. Signaling cascades were studied by immunoblot. TNF was stimulated by FcεRI ≈ ST2 > MRGPRX2. Surprisingly, neither FcεRI nor MRGPRX2 stimulation elicited NF-κB activation (IκB degradation, p65 phosphorylation) in stark contrast to IL-33. Accordingly, TNF production did not depend on NF-κB in FcεRI- or MRGPRX2-stimulated MCs, but did well so downstream of ST2. Conversely, ERK1/2 and PI3K were the crucial modules upon FcεRI/MRGPRX2 stimulation, while p38 was key to the IL-33-elicited route. The different signaling prerequisites were mirrored by their activation patterns with potent pERK/pAKT after FcεRI/MRGPRX2, but preferential induction of pp38/NF-κB downstream of ST2. FcεRI/MRGPRX2 strongly synergized with IL-33, and some synergy was still observed upon inhibition of each module (ERK1/2, JNK, p38, PI3K, NF-κB). IL-33's contribution to synergism was owed to p38 > JNK > NF-κB, while the partner receptor contributed through ERK > PI3K ≈ JNK. Concurrent IL-33 led to slightly prolonged pERK (downstream of MRGPRX2) or pAKT (activated by FcεRI), while the IL-33-elicited modules (pp38/NF-κB) remained unaffected by co-stimulation of FcεRI/MRGPRX2. Collectively, the strong synergistic activity of IL-33 primarily results from the complementation of highly distinct modules following co-activation of the partner receptor rather than by altered signal strength of the same modules.
Keywords: ERK; FcεRI; IL-33; JNK; MRGPRX2; NF-κB; PI3K; TNF-α; mast cells; p38.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokines Stimulated by IL-33 in Human Skin Mast Cells: Involvement of NF-κB and p38 at Distinct Levels and Potent Co-Operation with FcεRI and MRGPRX2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3580. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073580. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808264 Free PMC article.
-
MRGPRX2-Mediated Degranulation of Human Skin Mast Cells Requires the Operation of Gαi, Gαq, Ca++ Channels, ERK1/2 and PI3K-Interconnection between Early and Late Signaling.Cells. 2022 Mar 10;11(6):953. doi: 10.3390/cells11060953. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326404 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 and MRGPRX2-Triggered Activation of Human Skin Mast Cells-Elimination of Receptor Expression on Chronic Exposure, but Reinforced Degranulation on Acute Priming.Cells. 2019 Apr 11;8(4):341. doi: 10.3390/cells8040341. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30979016 Free PMC article.
-
MRGPRX2 signals its importance in cutaneous mast cell biology: Does MRGPRX2 connect mast cells and atopic dermatitis?Exp Dermatol. 2020 Nov;29(11):1104-1111. doi: 10.1111/exd.14182. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Exp Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32866307 Review.
-
MRGPRX2, drug pseudoallergies, inflammatory diseases, mechanisms and distinguishing MRGPRX2- and IgE/FcεRI-mediated events.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;89(11):3232-3246. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15845. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37430437 Review.
References
-
- Savinko T., Matikainen S., Saarialho-Kere U., Lehto M., Wang G., Lehtimaki S., Karisola P., Reunala T., Wolff H., Lauerma A., et al. IL-33 and ST2 in atopic dermatitis: Expression profiles and modulation by triggering factors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012;132:1392–1400. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Theoharides T.C., Zhang B., Kempuraj D., Tagen M., Vasiadi M., Angelidou A., Alysandratos K.D., Kalogeromitros D., Asadi S., Stavrianeas N., et al. IL-33 augments substance P-induced VEGF secretion from human mast cells and is increased in psoriatic skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:4448–4453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000803107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

