WAVE2 Regulates Actin-Dependent Processes Induced by the B Cell Antigen Receptor and Integrins
- PMID: 38067132
- PMCID: PMC10705906
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232704
WAVE2 Regulates Actin-Dependent Processes Induced by the B Cell Antigen Receptor and Integrins
Abstract
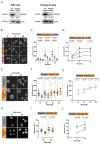
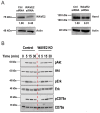
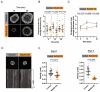
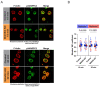
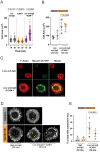
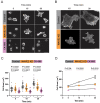
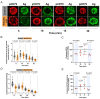
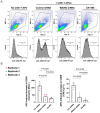
B cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling induces actin cytoskeleton remodeling by stimulating actin severing, actin polymerization, and the nucleation of branched actin networks via the Arp2/3 complex. This enables B cells to spread on antigen-bearing surfaces in order to increase antigen encounters and to form an immune synapse (IS) when interacting with antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Although the WASp, N-WASp, and WAVE nucleation-promoting factors activate the Arp2/3 complex, the role of WAVE2 in B cells has not been directly assessed. We now show that both WAVE2 and the Arp2/3 complex localize to the peripheral ring of branched F-actin when B cells spread on immobilized anti-Ig antibodies. The siRNA-mediated depletion of WAVE2 reduced and delayed B cell spreading on immobilized anti-Ig, and this was associated with a thinner peripheral F-actin ring and reduced actin retrograde flow compared to control cells. Depleting WAVE2 also impaired integrin-mediated B cell spreading on fibronectin and the LFA-1-induced formation of actomyosin arcs. Actin retrograde flow amplifies BCR signaling at the IS, and we found that depleting WAVE2 reduced microcluster-based BCR signaling and signal amplification at the IS, as well as B cell activation in response to antigen-bearing cells. Hence, WAVE2 contributes to multiple actin-dependent processes in B lymphocytes.
Keywords: Arp2/3 complex; B cell; B cell antigen receptor (BCR); F-actin; WAVE2; antigen presenting cell (APC); cell spreading; immune synapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WAVE2 regulates high-affinity integrin binding by recruiting vinculin and talin to the immunological synapse.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(17):5986-6000. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00136-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17591693 Free PMC article.
-
A B-cell actomyosin arc network couples integrin co-stimulation to mechanical force-dependent immune synapse formation.Elife. 2022 Apr 11;11:e72805. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72805. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35404237 Free PMC article.
-
N-WASP-dependent branched actin polymerization attenuates B-cell receptor signaling by increasing the molecular density of receptor clusters.Elife. 2023 Dec 12;12:RP87833. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87833. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38085658 Free PMC article.
-
The pivotal position of the actin cytoskeleton in the initiation and regulation of B cell receptor activation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):569-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23886914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WASP and WAVE family proteins: key molecules for rapid rearrangement of cortical actin filaments and cell movement.J Cell Sci. 2001 May;114(Pt 10):1801-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.10.1801. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11329366 Review.
Cited by
-
B cell mechanosensing regulates ER remodeling at the immune synapse.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 7;15:1464000. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464000. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39434873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham L., Wang J.C., Bolger-Munro M., Gold M.R. Structure, function, and spatial organization of the B cell receptor. In: Ratcliffe M.J.H., editor. Encyclopedia of Immunobiology. Volume 2. Elsivier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016. pp. 40–54. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

