The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38067147
- PMCID: PMC10706487
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232716
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Abstract
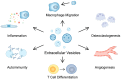
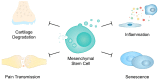
Cells can communicate with each other through extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are membrane-bound structures that transport proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. These structures have been found to mediate cellular differentiation and proliferation apoptosis, as well as inflammatory responses and senescence, among others. The cargo of these vesicles may include immunomodulatory molecules, which can then contribute to the pathogenesis of various diseases. By contrast, EVs secreted by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown important immunosuppressive and regenerative properties. Moreover, EVs can be modified and used as drug carriers to precisely deliver therapeutic agents. In this review, we aim to summarize the current evidence on the roles of EVs in the progression and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA), which are important and prevalent joint diseases with a significant global burden.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stem cells; osteoarthritis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenic or Therapeutic Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatic Diseases: Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 22;18(4):889. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040889. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28441721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1912. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01912. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Dec 1;18(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1178-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27906035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic prospects of microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive overview.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Mar;480(3):1275-1286. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05082-1. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39105963 Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Targets of Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022 Dec 30;11(12):1177-1185. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szac075. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36318277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles: immunomodulation, diagnosis, and promising therapeutic roles for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1499929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1499929. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39624102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNA in the Pathogenesis of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 1;25(11):6108. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116108. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perillyl alcohol promotes autophagy by suppressing the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway in osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 22;15(1):26549. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12274-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40695916 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial Fluid Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Severe Osteoarthritis Differentially Promote a Pro-Catabolic, Inflammatory Chondrocyte Phenotype.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 6;15(6):829. doi: 10.3390/biom15060829. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563469 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of current evidence.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):889-915. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01670-9. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40024954
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

