In Doxorubicin-Adapted Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells, Acquiring Multidrug Resistance and Improved Immunosuppressive Abilities, Doxorubicin Activity Was Enhanced by Chloroquine and GW4869
- PMID: 38067159
- PMCID: PMC10706762
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232732
In Doxorubicin-Adapted Hodgkin Lymphoma Cells, Acquiring Multidrug Resistance and Improved Immunosuppressive Abilities, Doxorubicin Activity Was Enhanced by Chloroquine and GW4869
Abstract
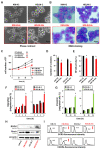
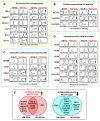
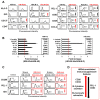
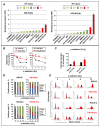
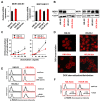
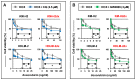
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is a highly curable disease (70-80%), even though long-term toxicities, drug resistance, and predicting clinical responses to therapy are major challenges in cHL treatment. To solve these problems, we characterized two cHL cell lines with acquired resistance to doxorubicin, KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx (HRSdx), generated from KM-H2 and HDLM-2 cells, respectively. HRSdx cells developed cross-resistance to vinblastine, bendamustin, cisplatin, dacarbazine, gemcitabine, brentuximab vedotin (BV), and γ-radiation. Both HDLM-2 and HDLM-2dx cells had intrinsic resistance to BV but not to the drug MMAE. HDLM-2dx acquired cross-resistance to caelyx. HRSdx cells had in common decreased CD71, CD80, CD54, cyt-ROS, HLA-DR, DDR1, and CD44; increased Bcl-2, CD58, COX2, CD26, CCR5, and invasive capability; increased CCL5, TARC, PGE2, and TGF-β; and the capability of hijacking monocytes. In HRSdx cells less sensitive to DNA damage and oxidative stress, the efflux drug transporters MDR1 and MRP1 were not up-regulated, and doxorubicin accumulated in the cytoplasm rather than in the nucleus. Both the autophagy inhibitor chloroquine and extracellular vesicle (EV) release inhibitor GW4869 enhanced doxorubicin activity and counteracted doxorubicin resistance. In conclusion, this study identifies common modulated antigens in HRSdx cells, the associated cross-resistance patterns, and new potential therapeutic options to enhance doxorubicin activity and overcome resistance.
Keywords: Hodgkin lymphoma; cross-resistance; doxorubicin; drug resistance; immunosuppression.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arlt A., von Bonin F., Rehberg T., Perez-Rubio P., Engelmann J.C., Limm K., Reinke S., Dullin C., Sun X., Specht R., et al. High CD206 Levels in Hodgkin Lymphoma-Educated Macrophages Are Linked to Matrix-Remodeling and Lymphoma Dissemination. Mol. Oncol. 2020;14:571–589. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12616. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dörsam B., Bösl T., Reiners K.S., Barnert S., Schubert R., Shatnyeva O., Zigrino P., Engert A., Hansen H.P., von Strandmann E.P. Hodgkin Lymphoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Change the Secretome of Fibroblasts Toward a CAF Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:1358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01358. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

