ATM/ATR Phosphorylation of CtIP on Its Conserved Sae2-like Domain Is Required for Genotoxin-Induced DNA Resection but Dispensable for Animal Development
- PMID: 38067190
- PMCID: PMC10706839
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232762
ATM/ATR Phosphorylation of CtIP on Its Conserved Sae2-like Domain Is Required for Genotoxin-Induced DNA Resection but Dispensable for Animal Development
Abstract
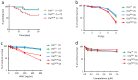
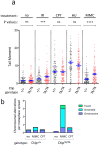
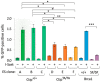
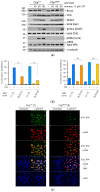
Homology-directed repair (HDR) of double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) is dependent on enzymatic resection of DNA ends by the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex. DNA resection is triggered by the CtIP/Sae2 protein, which allosterically promotes Mre11-mediated endonuclease DNA cleavage at a position internal to the DSB. Although the mechanics of resection, including the initial endonucleolytic step, are largely conserved in eucaryotes, CtIP and its functional counterpart in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sae2) share only a modest stretch of amino acid homology. Nonetheless, this stretch contains two highly conserved phosphorylation sites for cyclin-dependent kinases (T843 in mouse) and the damage-induced ATM/ATR kinases (T855 in mouse), both of which are required for DNA resection. To explore the function of ATM/ATR phosphorylation at Ctip-T855, we generated and analyzed mice expressing the Ctip-T855A mutant. Surprisingly, unlike Ctip-null mice and Ctip-T843A-expressing mice, both of which undergo embryonic lethality, homozygous CtipT855A/T855A mice develop normally. Nonetheless, they are hypersensitive to ionizing radiation, and CtipT855A/T855A mouse embryo fibroblasts from these mice display marked defects in DNA resection, chromosomal stability, and HDR-mediated repair of DSBs. Thus, although ATM/ATR phosphorylation of CtIP-T855 is not required for normal animal development, it enhances CtIP-mediated DNA resection in response to acute stress, such as genotoxin exposure.
Keywords: ATM/ATR phosphorylation; CtIP; DNA break repair; DNA resection; Mre11; genotoxic stress; homologous recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schaeper U., Subramanian T., Lim L., Boyd J.M., Chinnadurai G. Interaction between a cellular protein that binds to the C-terminal region of Adenovirus E1A (CtIP) and a novel cellular protein is disrupted by E1A through a conserved PLDLS motif. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:8549–8552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.15.8549. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

