New Insights into YAP/TAZ-TEAD-Mediated Gene Regulation and Biological Processes in Cancer
- PMID: 38067201
- PMCID: PMC10705714
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235497
New Insights into YAP/TAZ-TEAD-Mediated Gene Regulation and Biological Processes in Cancer
Abstract
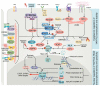
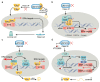
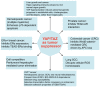
The Hippo pathway is conserved across species. Key mammalian Hippo pathway kinases, including MST1/2 and LATS1/2, inhibit cellular growth by inactivating the TEAD coactivators, YAP, and TAZ. Extensive research has illuminated the roles of Hippo signaling in cancer, development, and regeneration. Notably, dysregulation of Hippo pathway components not only contributes to tumor growth and metastasis, but also renders tumors resistant to therapies. This review delves into recent research on YAP/TAZ-TEAD-mediated gene regulation and biological processes in cancer. We focus on several key areas: newly identified molecular patterns of YAP/TAZ activation, emerging mechanisms that contribute to metastasis and cancer therapy resistance, unexpected roles in tumor suppression, and advances in therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway. Moreover, we provide an updated view of YAP/TAZ's biological functions, discuss ongoing controversies, and offer perspectives on specific debated topics in this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: TAZ; TEAD; YAP; cancer therapy; gene regulation; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Hippo Pathway Effectors YAP/TAZ-TEAD Oncoproteins as Emerging Therapeutic Targets in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 2;15(13):3468. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133468. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of transgenic lines to monitor and manipulate Yap/Taz-Tead activity in zebrafish reveals both evolutionarily conserved and divergent functions of the Hippo pathway.Mech Dev. 2014 Aug;133:177-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Mech Dev. 2014. PMID: 24560909 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of YAP/TAZ by the Hippo pathway and the Small GTPase pathway.Small GTPases. 2020 Jul;11(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1435986. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29457552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Irreversible TEAD Inhibitor, SWTX-143, Blocks Hippo Pathway Transcriptional Output and Causes Tumor Regression in Preclinical Mesothelioma Models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Jan 3;23(1):3-13. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0681. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 37748190
-
Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ-TEAD Biosensors.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 19;11(10):1596. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101596. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635084 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Statins as Secondary Preventive Agent to Limit Breast Cancer Metastatic Outgrowth.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 3;26(3):1300. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031300. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological modulation of stem cells signaling pathway for therapeutic applications.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04438-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40598543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs and Hippo signaling in non-small cell lung cancer: emerging roles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 18;16(1):1365. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03099-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40679672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLK1>Nek1 Axis Promotes Nuclear Retention and Activation of YAP with Implications for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;16(16):2918. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162918. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199688 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming and signaling adaptations in anoikis resistance: mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3315-3342. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05199-3. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39821582 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

