Bacteremia in Patients with Solid Organ Cancer: Insights into Epidemiology and Antibiotic Consumption
- PMID: 38067264
- PMCID: PMC10705097
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235561
Bacteremia in Patients with Solid Organ Cancer: Insights into Epidemiology and Antibiotic Consumption
Abstract
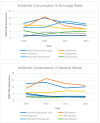
Epidemiology and risk factors associated to bacterial resistance in solid organ cancer (SOC) patients has been barely described. This retrospective monocentric study analyzed clinical variables in SOC patients who developed bacteremia between 1 January 2019 and 31 December 2022. We described rates of bacterial resistance in Gram negative bacteria (80.6%): E. coli-ESBL, K. pneumoniae-ESBL, Carbapenem-Resistant K. pneumoniae and Meropenem-Resistant P. aeruginosa, as well as antibiotic consumption, and compared these rates between the medical and oncology wards. In total, we included 314 bacteremias from 253 patients. SOC patients are frequently prescribed antibiotics (40.8%), mainly fluoroquinolones. Nosocomial bacteremia accounted for 18.2% of the cases and only 14.3% of patients were neutropenic. Hepatobiliary tract was the most frequent tumor (31.5%) and source of bacteremia (38.5%). Resistant bacteria showed a decreased rate of resistance during the years studied in the oncology ward. Both K-ESBL and K-CBP resistance rates decreased (from 45.8% to 20.0%, and from 29.2% to 20.0%, respectively), as well as MRPA, which varied from a resistance rate of 28% to 16.7%. The presence of a urinary catheter (p < 0.001) and previous antibiotic prescription (p = 0.002) were risk factors for bacterial resistance. Identifying either of these risk factors could help in guiding antibiotic prescription for SOC patients.
Keywords: antibiotic consumption; bacterial resistance; hospital co-management; hospitalist care; solid organ cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. World Health Organization Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023: 2021 Data. [(accessed on 14 April 2023)]. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2900/63495. - DOI
-
- Tian L., Tan R., Chen Y., Sun J., Liu J., Qu H., Wang X. Epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections in a teaching hospital: Factors related to the carbapenem resistance and patient mortality. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2016;5:48. doi: 10.1186/s13756-016-0145-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Velasco E., Byington R., Martins C.A.S., Schirmer M., Dias L.M.C., Gonçalves V.M.S.C. Comparative study of clinical characteristics of neutropenic and non-neutropenic adult cancer patients with bloodstream infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006;25:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s10096-005-0077-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources