Effects of Physical Activity Interventions on Self-Perceived Health Status among Lung Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38067317
- PMCID: PMC10705123
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235610
Effects of Physical Activity Interventions on Self-Perceived Health Status among Lung Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Patients with lung cancer may experience deterioration in quality of life due to adverse effects caused by their disease and its treatment. Although exercise programs have been shown to improve quality of life in certain stages of the disease, the overall impact on this population is unknown. The objective of this research was to evaluate the effect of physical activity on the self-perception of quality of life, physical wellbeing and dyspnea in lung cancer patients. Thirteen articles were included. Five meta-analyses were performed using the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) to evaluate the target outcomes. Results showed significant differences in quality of life (p = 0.01; SMD = 0.43, 95% CI = 0.10, 0.75), physical functioning (p = 0.01; SMD = 0.27, 95% CI = 0.06, 0.49) and physical wellbeing (p = 0.01; SMD = 0.37, 95% CI = 0.08, 0.67) in favour of participants who have undergone the programme compared to those who have not, without significant differences between the two groups in dyspnea. This study shows how physical activity interventions could have positive effects on physical functioning and physical wellbeing but could also be effective for improving quality of life in patients with lung cancer.
Keywords: different stages; dyspnoea; exercise; physical wellbeing; randomised control trial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

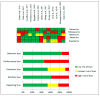



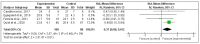

Similar articles
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training for advanced lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 11;2(2):CD012685. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012685.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30741408 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Exercise Interventions and Outcomes After Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Feb 1;4(2):e210254. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0254. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33635329 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise interventions on cancer-related fatigue and quality of life among cancer patients: a meta-analysis.BMC Nurs. 2023 Jun 13;22(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01363-0. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37312185 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training undertaken by people within 12 months of lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 17;6(6):CD009955. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009955.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31204439 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation between cancer cachexia and psychosocial impact in older patients with advanced lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025 Jan 23;12:100658. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2025.100658. eCollection 2025 Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40104042 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Benefits from Physical Exercise in Advanced Cancer Patients Undergoing Systemic Therapy? A Narrative Review of the Randomized Clinical Trials.Curr Oncol. 2024 Dec 1;31(12):7631-7646. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31120563. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39727686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perioperative respiratory physiotherapy in patients with thoracic tumors: Summary of best evidence and recommendations.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025 May 23;12:100730. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2025.100730. eCollection 2025 Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40547880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital health and physical activity: Insights from advanced lung cancer patients in Hong Kong.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025 Jul 19;12:100759. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2025.100759. eCollection 2025 Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40831612 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

