Inflammation and Immunity Gene Expression Patterns and Machine Learning Approaches in Association with Response to Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors-Based Treatments in Clear-Cell Renal Carcinoma
- PMID: 38067341
- PMCID: PMC10705515
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235637
Inflammation and Immunity Gene Expression Patterns and Machine Learning Approaches in Association with Response to Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors-Based Treatments in Clear-Cell Renal Carcinoma
Abstract
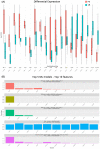
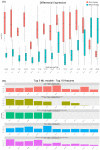
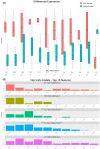
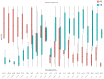
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common renal cancer. Despite the rapid evolution of targeted therapies, immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibition (ICI) as well as combination therapies, the cure of metastatic ccRCC (mccRCC) is infrequent, while the optimal use of the various novel agents has not been fully clarified. With the different treatment options, there is an essential need to identify biomarkers to predict therapeutic efficacy and thus optimize therapeutic approaches. This study seeks to explore the diversity in mRNA expression profiles of inflammation and immunity-related circulating genes for the development of biomarkers that could predict the effectiveness of immunotherapy-based treatments using ICIs for individuals with mccRCC. Gene mRNA expression was tested by the RT2 profiler PCR Array on a human cancer inflammation and immunity crosstalk kit and analyzed for differential gene expression along with a machine learning approach for sample classification. A number of mRNAs were found to be differentially expressed in mccRCC with a clinical benefit from treatment compared to those who progressed. Our results indicate that gene expression can classify these samples with high accuracy and specificity.
Keywords: TKIs; cancer; ccRCC; immunotherapy; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor Microenvironment Features as Predictive Biomarkers of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) in Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (mccRCC).Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 10;13(2):231. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020231. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33435262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and emerging first-line systemic therapies in metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.J BUON. 2019 Jul-Aug;24(4):1340-1353. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31646776 Review.
-
Outcomes of patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with second-line VEGFR-TKI after first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Jun;114:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 May 7. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31075726 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapies in clinical trials for renal cell carcinoma: how could they impact future treatments?Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021 Dec;30(12):1221-1229. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.2014814. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34875200
-
Immune-Associated Gene Signatures Serve as a Promising Biomarker of Immunotherapeutic Prognosis for Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 May 24;13:890150. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.890150. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35686121 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of Cuproptosis-related lncRNAS in Patients Receiving Immunotherapy for Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Indicates Progressive Disease.In Vivo. 2025 Jan-Feb;39(1):146-151. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13812. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 39740865 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Therapeutic Response Prediction for Ustekinumab in Ulcerative Colitis Using an Ensemble Bioinformatics Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 18;25(10):5532. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105532. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arora R.D., Limaiem F. StatPearls. StatPearls; Tampa, FL, USA: 2023. Renal Clear Cell Cancer. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

