Breast Cancer Treatment: To tARget or Not? That Is the Question
- PMID: 38067367
- PMCID: PMC10705204
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235664
Breast Cancer Treatment: To tARget or Not? That Is the Question
Abstract
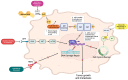
To assess AR's role in TNBC treatment, various existing and completed clinical trials targeting AR or co-targeting AR with other pertinent signaling molecules were analyzed. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6), cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17 lyase), and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway were some of the most prevalent biomarkers used in combination therapy with AR inhibitors in these trials. Studying how AR functions in tandem with these molecules can have increasing breakthroughs in the treatment options for TNBC. Previous studies have been largely unsuccessful in utilizing AR as the sole drug target for systemic targeted treatment in TNBC. However, there is a lack of other commonly used drug target biomarkers in the treatment of this disease, as well. Thus, analyzing the clinical benefit rate (CBR) within clinical trials that use combination therapy can prove to be imperative to the progression of improving treatment options and prognoses.
Keywords: AR; CDK4/6; CYP17 lyase; DHT; ER; HER2; PI3K/AKT; PR; TNBC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgen receptor in breast cancer and its clinical implication.Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 31;4:30. doi: 10.21037/tbcr-23-44. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37946721 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Combined Androgen Receptor Antagonism and Cell Cycle Inhibition in Androgen Receptor Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Jun;20(6):1062-1071. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0807. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 33722849 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of the PI3K pathway inhibitor plus cell cycle pathway inhibitor to combat endocrine resistance in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: a genomic algorithm-based treatment approach.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 1;8(12):2359-2376. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30662797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of androgen receptor inhibitor enzalutamide with the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib in triple negative breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 22;17(12):e0279522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279522. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36548336 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Treatment Strategies, Unmet Needs, and Potential Targets for Future Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 24;12(9):2392. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092392. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32846967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic targeting of regulatory T cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma: new horizons in immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 19;23(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02193-7. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39696340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lim E., Brufsky A., Rugo H.S., Vogel C.L., O’Shaugnessy J., Getzenber R.H., Barnette K.G., Rodriguez D., Bird G., Steiner M.S., et al. Phase 3 ENABLAR-2 study to evaluate enobosarm and abemaciclib combination compared to estrogen-blocking agent for the second-line treatment of AR+, ER+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer in patients who previously received palbociclib and estrogen-blocking agent combination therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:TPS1121.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

