Identification of SPP1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Immune Cells Modulator in Urothelial Bladder Cancer: A Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 38067407
- PMCID: PMC10705199
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15235704
Identification of SPP1 as a Prognostic Biomarker and Immune Cells Modulator in Urothelial Bladder Cancer: A Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
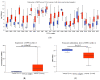
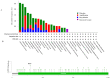
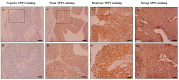
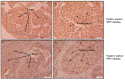
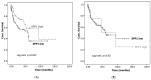
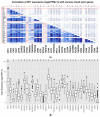
Secreted phosphoprotein-1 (SPP1) expression is differentially altered in many malignancies and could serve as a potential prognostic biomarker. Recent findings indicated that SPP1 possesses a broader role in bladder cancer (BC) pathogenesis than previously envisioned; however, the underlying mechanisms governing its expression, cellular localization, prognostic value and immune-related role in bladder cancer remain poorly understood. The expression and the prognosis value of SPP1 were assessed using immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining on a tissue microarray. SPP1 expression was correlated with the clinicopathological parameters, and survival analysis was calculated using a Kaplan-Meier plotter. Bioinformatics analysis of TCGA data was queried using UALCAN, CIBERSORT and TIMER datasets to decipher the biological processes enrichment pattern, protein-protein interactions and characterize tumor-infiltrating immune cells, respectively. IHC revealed that SPP1 expression is significantly associated with tumor type, stage, grade and smoking status. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed that low SPP1 expression is an unfavorable prognostic indicator in bladder cancer patients (p = 0.02, log-rank). The significant increased expression of the SPP1 level is associated with evident hypomethylation of the gene promoter in cancer compared to normal tissues in the TCGA-bladder dataset. Missense mutation is the most frequent genetic alteration of the SPP1 gene. Protein-protein interactions demonstrated that SPP1 shares the same network with many important genes and is involved in many signaling pathways and biological processes. TIMER reported a significant correlation between SPP1 expression and multiple immune cells infiltration. Furthermore, the expression of SPP1 was found to be positively correlated with a number of immune checkpoint genes such as PD-1 and CTLA4. The current investigation indicates that the SPP1 protein could serve as a prognostic biomarker and merit further investigation to validate its clinical usefulness in patients with bladder cancer.
Keywords: SPP1; bioinformatics; biomarker; bladder cancer; immune infiltration; prognostic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SPP1 is a prognostic related biomarker and correlated with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in ovarian cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 30;22(1):1367. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10485-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36585688 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of COL10A1 and its correlation with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in urothelial bladder cancer: A comprehensive study based on bioinformatics and clinical analysis validation.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:955949. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.955949. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006317 Free PMC article.
-
The Correlation Between SPP1 and Immune Escape of EGFR Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma Was Explored by Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 10;11:592854. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.592854. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34178613 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis to Identify SPP1 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Cervical Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 4;12:732822. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.732822. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35058964 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and Predictive Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Urothelial Cancer of the Bladder.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;12(9):2692. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092692. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SPP1 mRNA Expression Is Associated with M2 Macrophage Infiltration and Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 25;46(12):13499-13513. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120806. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727934 Free PMC article.
-
NOTCH3 promotes malignant progression of bladder cancer by directly regulating SPP1 and activating PI3K/AKT pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Nov 18;15(11):840. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07241-0. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39557868 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of KEAP1/NFE2L2 alterations across 3600+ tumors reveals an NRF2 expression signature as a prognostic biomarker in cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Aug 18;9(1):291. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-01088-0. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40825842 Free PMC article.
-
SPP1 promotes tumor progression in esophageal carcinoma by activating focal adhesion pathway.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 30;15(3):818-828. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-302. Epub 2024 Jun 27. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38989403 Free PMC article.
-
SPP1A and VEGFC splice isoforms as predictive diagnostic biomarkers for high and low-grade bladder cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2025 Apr 25;13(2):156-168. doi: 10.62347/XXIY2093. eCollection 2025. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2025. PMID: 40400998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain S.A., Porta N., Hall E., Salawu A., Lewis R., Sreenivasan T., Wallace J., Crundwell M., Jenkins P., Tremlett J., et al. Outcomes in Patients with Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Followed by (Chemo)radiotherapy in the BC2001 Trial. Eur. Urol. 2020;79:307–315. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.11.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Witjes J.A., Bruins H.M., Cathomas R., Compérat E.M., Cowan N.C., Gakis G., Hernández V., Espinós E.L., Lorch A., Neuzillet Y., et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021;79:82–104. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

