Effusanin B Inhibits Lung Cancer by Prompting Apoptosis and Inhibiting Angiogenesis
- PMID: 38067413
- PMCID: PMC10707445
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237682
Effusanin B Inhibits Lung Cancer by Prompting Apoptosis and Inhibiting Angiogenesis
Abstract
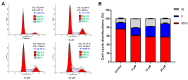
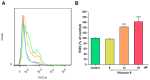
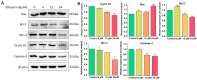
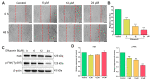
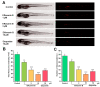
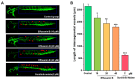
Cancer is one of the deadliest human diseases, causing high rates of illness and death. Lung cancer has the highest mortality rate among all malignancies worldwide. Effusanin B, a diterpenoid derived from Isodon serra, showed therapeutic potential in treating non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Further research on the mechanism indicated that effusanin B inhibited the proliferation and migration of A549 cells both in vivo and in vitro. The in vitro activity assay demonstrated that effusanin B exhibited significant anticancer activity. Effusanin B induced apoptosis, promoted cell cycle arrest, increased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and altered the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Based on mechanistic studies, effusanin B was found to inhibit the proliferation and migration of A549 cells by affecting the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) pathways. Moreover, effusanin B inhibited tumor growth and spread in a zebrafish xenograft model and demonstrated anti-angiogenic effects in a transgenic zebrafish model.
Keywords: FAK; STAT3; angiogenesis; anti-tumor; diterpenoid; effusanin B; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



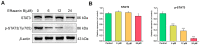
References
-
- Li H., Wang Y., Shao S., Yu H., Wang D., Li C., Wang S. Rabdosia serra alleviates dextran sulfate sodium salt-induced colitis in mice through anti-inflammation, regulating Th17/Treg balance, maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, and modulating gut microbiota. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022;12:824–838. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2022.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Committee for the editing of Chinese Materia Medica, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine . Chinese Materia Medica (VII) 1st ed. Shanghai Science and Technology Press; Shanghai, China: 1999. pp. 154–156.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

