Cannabis as a Source of Approved Drugs: A New Look at an Old Problem
- PMID: 38067416
- PMCID: PMC10707504
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237686
Cannabis as a Source of Approved Drugs: A New Look at an Old Problem
Abstract
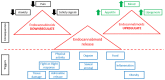
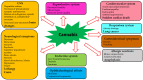
Cannabis plants have been used in medicine since ancient times. They are well known for their anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-cancer, anti-oxidative, anti-microbial, anti-viral, and anti-fungal activities. A growing body of evidence indicates that targeting the endocannabinoid system and various other receptors with cannabinoid compounds holds great promise for addressing multiple medical conditions. There are two distinct avenues in the development of cannabinoid-based drugs. The first involves creating treatments directly based on the components of the cannabis plant. The second involves a singular molecule strategy, in which specific phytocannabinoids or newly discovered cannabinoids with therapeutic promise are pinpointed and synthesized for future pharmaceutical development and validation. Although the therapeutic potential of cannabis is enormous, few cannabis-related approved drugs exist, and this avenue warrants further investigation. With this in mind, we review here the medicinal properties of cannabis, its phytochemicals, approved drugs of natural and synthetic origin, pitfalls on the way to the widespread clinical use of cannabis, and additional applications of cannabis-related products.
Keywords: cannabidiol; cannabis; drugs; tetrahydrocannabinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Klionsky D.J., Abdel-Aziz A.K., Abdelfatah S., Abdellatif M., Abdoli A., Abel S., Abeliovich H., Abildgaard M.H., Abudu Y.P., Acevedo-Arozena A., et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition) Autophagy. 2021;17:1–382. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1797280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H.-L. An archaeological and historical account of cannabis in China. Econ. Bot. 1973;28:437–448. doi: 10.1007/BF02862859. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources