Quality Assurance Investigations and Impurity Characterization during Upscaling of [177Lu]Lu-PSMAI&T
- PMID: 38067427
- PMCID: PMC10707575
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237696
Quality Assurance Investigations and Impurity Characterization during Upscaling of [177Lu]Lu-PSMAI&T
Abstract
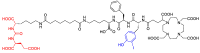
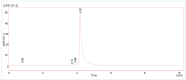
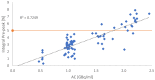
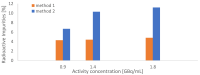
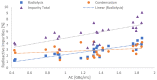
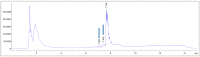
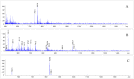
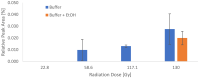
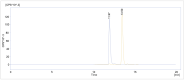
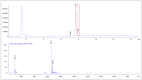
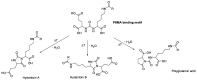
[177Lu]Lu-PSMAI&T is widely used for the radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Since this kind of therapy has gained a large momentum in recent years, an upscaled production process yielding multiple patient doses in one batch has been developed. During upscaling, the established production method as well as the HPLC quality control were challenged. A major finding was a correlation between the specific activity and the formation of a pre-peak, presumably caused by radiolysis. Hence, nonradioactive reference standards were irradiated with an X-ray source and the formed pre-peak was subsequently identified as a deiodination product by UPLC-MS. To confirm the occurrence of the same deiodinated side product in the routine batch, a customized deiodinated precursor was radiolabeled and analyzed with the same HPLC setup, revealing an identical retention time to the pre-peak in the formerly synthesized routine batches. Additionally, further cyclization products of [177Lu]Lu-PSMAI&T were identified as major contributors to radiochemical impurities. The comparison of two HPLC methods showed the likelihood of the overestimation of the radiochemical purity during the synthesis of [177Lu]Lu-PSMAI&T. Finally, a prospective cost reduction through an optimization of the production process was shown.
Keywords: HPLC; UPLC-MS; [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T; quality assurance; radioligand therapy; radiolysis; upscaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

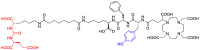
Similar articles
-
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Radioligand Therapy Using 177Lu-PSMA I&T and 177Lu-PSMA-617 in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Safety, Biodistribution, and Dosimetry.J Nucl Med. 2022 Aug;63(8):1199-1207. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262713. Epub 2021 Dec 9. J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 34887335 Free PMC article.
-
Examining Absorbed Doses of Indigenously Developed 177Lu-PSMA-617 in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients at Baseline and During Course of Peptide Receptor Radioligand Therapy.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021 Apr;36(3):292-304. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.3640. Epub 2020 May 5. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021. PMID: 32379495
-
Molecular imaging and biochemical response assessment after a single cycle of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-617/[177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 tandem therapy in mCRPC patients who have progressed on [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 monotherapy.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 16;11(9):4050-4060. doi: 10.7150/thno.56211. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754047 Free PMC article.
-
Update on radioligand therapy with 177Lu-PSMA for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: clinical aspects and survival effects.Tumori. 2022 Aug;108(4):315-325. doi: 10.1177/03008916211037732. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Tumori. 2022. PMID: 34405748 Review.
-
[177Lu]Lu-PSMA-Radioligand Therapy Efficacy Outcomes in Taxane-Naïve Versus Taxane-Treated Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis.J Nucl Med. 2023 Aug;64(8):1266-1271. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.265414. Epub 2023 May 11. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37169534
Cited by
-
Multifactorial analysis of radiochemical purity in high-activity 177Lu-labeled theranostics: impact of precursor source, 177Lu form, and production parameters.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025 Jul 22;10(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s41181-025-00372-5. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025. PMID: 40696084 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of End-of-Synthesis Radiochemical Purity of 177Lu-DOTA-PSMA-Ligands with Alternative Synthesis Approaches: Conversion Upswing and Side-Products Minimization.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Nov 30;16(12):1535. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121535. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39771514 Free PMC article.
-
A scalable protocol for the radiosynthesis of clinical grade lutetium-177-labeled theranostic agents.Nat Protoc. 2025 May 27. doi: 10.1038/s41596-025-01176-2. Online ahead of print. Nat Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40425733 Review.
-
Highlight selection of radiochemistry and radiopharmacy developments by editorial board.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Sep 16;9(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s41181-024-00296-6. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 39283414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pubchem Entry for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T. [(accessed on 15 September 2023)]; Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Unii-G5B860B0G1#section=NCI-Th....
-
- Sadaghiani M.S., Sheikhbahaei S., Werner R.A., Pienta K.J., Pomper M.G., Solnes L.B., Gorin M.A., Wang N.Y., Rowe S.P. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Effectiveness and Toxicities of Lutetium-177-labeled Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen-targeted Radioligand Therapy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021;80:82–94. - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency Pluvicto Entry European Medicines Agency. [(accessed on 30 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/pluvicto.
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA Approves Pluvicto for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer 2022. [(accessed on 16 September 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-appro....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

