In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Cancer Activity of Lasiokaurin in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Model
- PMID: 38067432
- PMCID: PMC10707582
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237701
In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Cancer Activity of Lasiokaurin in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Model
Abstract
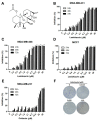
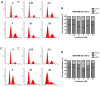
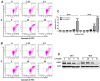
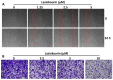
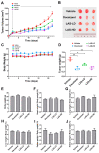
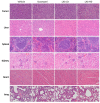
Due to its intricate heterogeneity, high invasiveness, and poor prognosis, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) stands out as the most formidable subtype of breast cancer. At present, chemotherapy remains the prevailing treatment modality for TNBC, primarily due to its lack of estrogen receptors (ERs), progesterone receptors (PRs), and human epidermal growth receptor 2 (HER2). However, clinical chemotherapy for TNBC is marked by its limited efficacy and a pronounced incidence of adverse effects. Consequently, there is a pressing need for novel drugs to treat TNBC. Given the rich repository of diverse natural compounds in traditional Chinese medicine, identifying potential anti-TNBC agents is a viable strategy. This study investigated lasiokaurin (LAS), a natural diterpenoid abundantly present in Isodon plants, revealing its significant anti-TNBC activity both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, LAS treatment induced cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and DNA damage in TNBC cells, while concurrently inhibiting cell metastasis. In addition, LAS effectively inhibited the activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) pathway and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), thus establishing its potential for multitarget therapy against TNBC. Furthermore, LAS demonstrated its ability to reduce tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model without exerting detrimental effects on the body weight or vital organs, confirming its safe applicability for TNBC treatment. Overall, this study shows that LAS is a potent candidate for treating TNBC.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt/mTOR; STAT3; isodon; lasiokaurin; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calycosin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through down-regulation of the novel estrogen receptor-α splice variant ER-α30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154924. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154924. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37393829
-
XS-2, a novel potent dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, exhibits high in vitro and in vivo anti-breast cancer activity and low toxicity with the potential to inhibit the invasion and migration of triple-negative breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Nov;155:113537. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113537. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36113258
-
Anti-tumor and anti-metastasis efficacy of E6201, a MEK1 inhibitor, in preclinical models of triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jun;175(2):339-351. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05166-3. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30826934 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin-induced apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Med Oncol. 2022 Oct 8;39(12):248. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01856-z. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36209343 Review.
-
Kinase inhibitors for precision therapy of triple-negative breast cancer: Progress, challenges, and new perspectives on targeting this heterogeneous disease.Cancer Lett. 2022 Oct 28;547:215775. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215775. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35667515 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of breast Cancer.Mol Cancer. 2025 Aug 1;24(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02416-5. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40750898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garrido-Castro A.C., Lin N.U., Polyak K. Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:176–198. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- E-ABCT-BBBB-3/the Research Centre for Chinese Medicine Innovation of The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univer-sity
- P0036741/The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Start-up Fund
- P0038596/The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Start-up Fund
- JA21026/Chongqing Science and Technology Commission
- JCYJ20220531090802006/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

