Occurrence of Luteolin in the Greek Flora, Isolation of Luteolin and Its Action for the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases
- PMID: 38067450
- PMCID: PMC10707704
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237720
Occurrence of Luteolin in the Greek Flora, Isolation of Luteolin and Its Action for the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases
Abstract
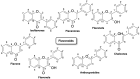
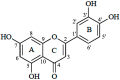
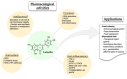
Higher plants possess the ability to synthesize a great number of compounds with many different functions, known as secondary metabolites. Polyphenols, a class of flavonoids, are secondary metabolites that play a crucial role in plant adaptation to both biotic and abiotic environments, including UV radiation, high light intensity, low/high temperatures, and attacks from pathogens, among others. One of the compounds that has received great attention over the last few years is luteolin. The objective of the current paper is to review the extraction and detection methods of luteolin in plants of the Greek flora, as well as their luteolin content. Furthermore, plant species, crop management and environmental factors can affect luteolin content and/or its derivatives. Luteolin exhibits various biological activities, such as cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antibacterial ones. As a result, luteolin has been employed as a bioactive molecule in numerous applications within the food industry and the biomedical field. Among the different available options for managing periodontitis, dental care products containing herbal compounds have been in the spotlight owing to the beneficial pharmacological properties of the bioactive ingredients. In this context, luteolin's anti-inflammatory activity has been harnessed to combat periodontal disease and promote the restoration of damaged bone tissue.
Keywords: aromatic; extraction; medicinal plants; pharmaceutical use; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: A brief review.Brain Res Bull. 2015 Oct;119(Pt A):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Brain Res Bull. 2015. PMID: 26361743 Review.
-
Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by luteolin: cardioprotective role in rat cardiomyocytes following ischemia/reperfusion.Nutrients. 2012 Dec 12;4(12):2008-19. doi: 10.3390/nu4122008. Nutrients. 2012. PMID: 23235403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Luteolin, inflammation and cancer: Special emphasis on gut microbiota.Biofactors. 2021 Mar;47(2):181-189. doi: 10.1002/biof.1710. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33507594 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:342-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.05.019. Epub 2018 May 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29801717 Review.
-
Luteolin ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice via suppressing macrophage activation and chemotaxis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Nov;124(Pt B):110996. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110996. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37776768
Cited by
-
Cenostigma bracteosum Hydroethanolic Extract: Chemical Profile, Antibacterial Activity, Cytotoxicity, and Gel Formulation Development.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 14;17(6):780. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060780. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574092 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into luteolin and its biological and pharmacological activities.EXCLI J. 2024 May 16;23:787-794. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7168. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 39165588 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Involvement of Glycerophospholipids in Susceptibility of Maize to Gibberella Root Rot Revealed by Comparative Metabolomics and Mass Spectrometry Imaging Joint Analysis.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 1;14(9):1376. doi: 10.3390/plants14091376. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- González-Sarrías A., Tomás-Barberán F.A., García-Villalba R. Structural Diversity of Polyphenols and Distribution in Foods. Diet. Polyphen. Their Metab. Health Eff. 2020:1–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials