Spectrophotometric Study of Charge-Transfer Complexes of Ruxolitinib with Chloranilic Acid and 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone: An Application to the Development of a Green and High-Throughput Microwell Method for Quantification of Ruxolitinib in Its Pharmaceutical Formulations
- PMID: 38067605
- PMCID: PMC10708051
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237877
Spectrophotometric Study of Charge-Transfer Complexes of Ruxolitinib with Chloranilic Acid and 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone: An Application to the Development of a Green and High-Throughput Microwell Method for Quantification of Ruxolitinib in Its Pharmaceutical Formulations
Abstract
Ruxolitinib (RUX) is a potent drug that has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and graft-versus-host disease. This study describes the formation of colored charge-transfer complexes (CTCs) of RUX, an electron donor, with chloranilic acid (CLA) and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ), the π-electron acceptors. The CTCs were characterized using UV-visible spectrophotometry. The formation of CTCs in methanol was confirmed via formation of new absorption bands with maximum absorption at 530 and 470 nm for CTCs with CLA and DDQ, respectively. The molar absorptivity and other physicochemical and electronic properties of CTCs were determined. The molar ratio was found to be 1:1 for both CTCs with CLA and CTCs with DDQ. The site of interaction on RUX molecules was assigned and the mechanisms of the reactions were postulated. The reactions were employed as basis for the development of a novel green and one-step microwell spectrophotometric method (MW-SPM) for high-throughput quantitation of RUX. Reactions of RUX with CLA and DDQ were carried out in 96-well transparent plates, and the absorbances of the colored CTCs were measured by an absorbance microplate reader. The MW-SPM was validated according to the ICH guidelines. The limits of quantitation were 7.5 and 12.6 µg/mL for the methods involving reactions with CLA and DDQ, respectively. The method was applied with great reliability to the quantitation of RUX content in Jakavi® tablets and Opzelura® cream. The greenness of the MW-SPM was assessed by three different metric tools, and the results proved that the method fulfills the requirements of green analytical approaches. In addition, the one-step reactions and simultaneous handling of a large number of samples with micro-volumes using the proposed method enables the high-throughput analysis. In conclusion, this study describes the first MW-SPM, a valuable analytical tool for the quality control of pharmaceutical formulations of RUX.
Keywords: charge-transfer complex; green and high-throughput approach; microwell spectrophotometry; quality control; ruxolitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
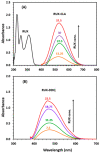
 ) and DDQ (
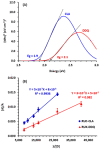
) and DDQ ( ). The values are the means of 3 measurements ± SD. Panel (B) a molecule of RUX with atom numbers, and the arrows pointing to the potential atoms for participation in the formation of CTCs, along with their partial charges. Negative sign denotes negative electron density.
). The values are the means of 3 measurements ± SD. Panel (B) a molecule of RUX with atom numbers, and the arrows pointing to the potential atoms for participation in the formation of CTCs, along with their partial charges. Negative sign denotes negative electron density.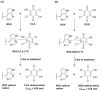
 ) and DDQ (
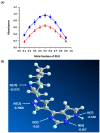
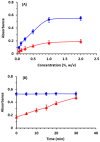
) and DDQ ( ). The points are the means of 3 determinations ± SD.
). The points are the means of 3 determinations ± SD.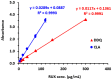

Similar articles
-
Green and High Throughput Assay Using 96-Microwell Base to Determine Metformin Hydrochloride in the Tablet Dosage Form.Int J Anal Chem. 2024 Aug 23;2024:3374034. doi: 10.1155/2024/3374034. eCollection 2024. Int J Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39376695 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Two Novel One-Step and Green Microwell Spectrophotometric Methods for High-Throughput Determination of Ceritinib, a Potent Drug for Treatment of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 12;59(10):1813. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101813. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893531 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Two Eco-Friendly and High-Throughput Microwell Spectrophotometric Methods for Analysis of an Antibacterial Drug Tulathromycin in Pharmaceutical Bulk Form.J AOAC Int. 2024 Jul 4;107(4):538-548. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsae035. J AOAC Int. 2024. PMID: 38652601
-
Spectrophotometric and computational investigations of charge transfer complexes of chloranilic acid with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and application to development of novel universal 96-microwell assay for their determination in pharmaceutical formulations.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 May 5;252:119482. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119482. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 33571740
-
DDQ as a versatile and easily recyclable oxidant: a systematic review.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 8;11(47):29826-29858. doi: 10.1039/d1ra04575j. eCollection 2021 Sep 1. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green and High Throughput Assay Using 96-Microwell Base to Determine Metformin Hydrochloride in the Tablet Dosage Form.Int J Anal Chem. 2024 Aug 23;2024:3374034. doi: 10.1155/2024/3374034. eCollection 2024. Int J Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39376695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FDA. U.S. Food & Drug Administration FDA Approves Treatment for Patients with Rare Bone Marrow Disorder. [(accessed on 7 October 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-treatme....
-
- Jakavi (ruxolitinib) Tablets [Highlights of Prescribing Information]. Wilmington, DE: Incyte Corporation. [(accessed on 7 October 2023)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/202192lbl.pdf.
-
- FDA. U.S. Food & Drug Administration FDA Approves Ruxolitinib for Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease. [(accessed on 7 October 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-appro....
-
- FDA. U.S. Food & Drug Administration FDA Approves Ruxolitinib for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease. [(accessed on 7 October 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-appro....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

