Natural Products for Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury: A Review
- PMID: 38067630
- PMCID: PMC10708418
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28237901
Natural Products for Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury: A Review
Abstract
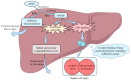
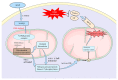
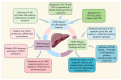
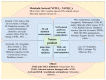
The liver plays a vital role in metabolism, synthesis, and detoxification, but it is susceptible to damage from various factors such as viral infections, drug reactions, excessive alcohol consumption, and autoimmune diseases. This susceptibility is particularly problematic for patients requiring medication, as drug-induced liver injury often leads to underestimation, misdiagnosis, and difficulties in treatment. Acetaminophen (APAP) is a widely used and safe drug in therapeutic doses but can cause liver toxicity when taken in excessive amounts. This study aimed to investigate the hepatotoxicity of APAP and explore potential treatment strategies using a mouse model of APAP-induced liver injury. The study involved the evaluation of various natural products for their therapeutic potential. The findings revealed that natural products demonstrated promising hepatoprotective effects, potentially alleviating liver damage and improving liver function through various mechanisms such as oxidative stress and inflammation, which cause changes in signaling pathways. These results underscore the importance of exploring novel treatment options for drug-induced liver injury, suggesting that further research in this area could lead to the development of effective preventive and therapeutic interventions, ultimately benefiting patients with liver injury caused by medicine.
Keywords: P450 enzymes; acetaminophen; acute liver injury; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of Farnesoid X Receptor by Schaftoside Ameliorates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Jul 10;33(2):87-116. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7791. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 32037847
-
Shikonin attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108704. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108704. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30818140
-
Pectolinarigenin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory response in Nrf2 and PPARa dependent manners.Phytomedicine. 2023 May;113:154726. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154726. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36863308
-
Autophagy and acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2018 Jul;92(7):2153-2161. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2237-5. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29876591 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Plants and Plant Derived Phytochemicals against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 28;19(12):3776. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123776. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30486484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactate Metabolism and Lactylation Modification: New Opportunities and Challenges in Cardiovascular Disease.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 1;6(7):e70269. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70269. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40599233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvianolic Acid B Alleviates Liver Injury by Regulating Lactate-Mediated Histone Lactylation in Macrophages.Molecules. 2024 Jan 1;29(1):236. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010236. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38202819 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

