The Challenges and Advantages of Distributed Fiber Optic Strain Monitoring in and on the Cementitious Matrix of Concrete Beams
- PMID: 38067850
- PMCID: PMC10708809
- DOI: 10.3390/s23239477
The Challenges and Advantages of Distributed Fiber Optic Strain Monitoring in and on the Cementitious Matrix of Concrete Beams
Abstract
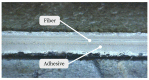
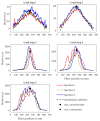
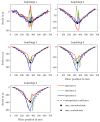
Distributed fiber optic strain measurement techniques have become increasingly important in recent years, especially in the field of structural health monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Numerous publications show the various monitoring possibilities from bridges to special heavy structures. The present study is intended to demonstrate the possibilities, but also the challenges, of distributed fiber optic strain measurement in reinforced concrete structures. For this purpose, concrete beams for 3-point bending tests were equipped with optical fibers on the reinforcement and concrete surface as well as in the concrete matrix in order to record the strains in the compression and tension zone. In parallel, an analytical approach based on the maximum strains in the uncracked and cracked states was performed using the Eurocode 2 interpolation coefficient. In principle, the structural design correlates with the measured values, but the strains are underestimated, especially in the cracked zone. During load increase, structural distortions in the compression zone affected the strain signal, making reliable evaluation in this zone difficult. The information content of distributed fiber optic strain measurement in reinforced concrete structures can offer tremendous opportunities. Future research should consider all aspects of the bond, sensor selection and positioning. In addition, there is a lack of information on the long-term stability of the joint and the fiber coating, as well as the effects of dynamic loading.
Keywords: cementitious matrix; concrete beams; distributed fiber optic strain monitoring; structural health monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Determination of the Real Cracking Moment of Two Reinforced Concrete Beams Through the Use of Embedded Fiber Optic Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Feb 10;20(3):937. doi: 10.3390/s20030937. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32050667 Free PMC article.
-
Strain Sharing Assessment in Woven Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Sep 22;16(10):1564. doi: 10.3390/s16101564. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27669251 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Performance of Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors Embedded in Reinforced Concrete Beams under Sustained Deflection and Cyclic Loading.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 22;21(19):6338. doi: 10.3390/s21196338. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34640657 Free PMC article.
-
Fiber Optic Sensors Embedded in Textile-Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structural Health Monitoring: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 21;21(15):4948. doi: 10.3390/s21154948. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34372185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bond-Slip Monitoring of Concrete Structures Using Smart Sensors-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 11;19(5):1231. doi: 10.3390/s19051231. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30862071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Liquids and Saturated Salt Solutions on Polymer-Coated Fiber Optic Sensors for Distributed Strain and Temperature Measurement.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;24(14):4659. doi: 10.3390/s24144659. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066056 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Data Pre-Processing Methods for Distributed Fiber Optic Strain Sensing.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;24(23):7454. doi: 10.3390/s24237454. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39685991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becks H., Baktheer A., Marx S., Classen M., Hegger J., Chudoba R. Monitoring concept for the propagation of compressive fatigue in externally prestressed concrete beams using digital image correlation and fiber optic sensors. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2023;46:514–526. doi: 10.1111/ffe.13881. - DOI
-
- Minardo A., Persichetti G., Testa G., Zeni L., Bernini R. Long term structural health monitoring by Brillouin fibre-optic sensing: A real case. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012;9:S64–S69. doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/9/4/S64. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

