Advancements in Home-Based Devices for Detecting Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Comprehensive Study
- PMID: 38067885
- PMCID: PMC10708697
- DOI: 10.3390/s23239512
Advancements in Home-Based Devices for Detecting Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Comprehensive Study
Abstract
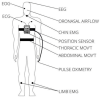
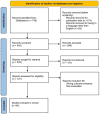
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a respiratory disorder characterized by frequent breathing pauses during sleep. The apnea-hypopnea index is a measure used to assess the severity of sleep apnea and the hourly rate of respiratory events. Despite numerous commercial devices available for apnea diagnosis and early detection, accessibility remains challenging for the general population, leading to lengthy wait times in sleep clinics. Consequently, research on monitoring and predicting OSA has surged. This comprehensive paper reviews devices, emphasizing distinctions among representative apnea devices and technologies for home detection of OSA. The collected articles are analyzed to present a clear discussion. Each article is evaluated according to diagnostic elements, the implemented automation level, and the derived level of evidence and quality rating. The findings indicate that the critical variables for monitoring sleep behavior include oxygen saturation (oximetry), body position, respiratory effort, and respiratory flow. Also, the prevalent trend is the development of level IV devices, measuring one or two signals and supported by prediction software. Noteworthy methods showcasing optimal results involve neural networks, deep learning, and regression modeling, achieving an accuracy of approximately 99%.
Keywords: actigraphy; oximetry; respiratory effort; respiratory flow; sleep apnea detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep-Learning Model Based on Convolutional Neural Networks to Classify Apnea-Hypopnea Events from the Oximetry Signal.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1384:255-264. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06413-5_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36217089
-
Devices for home detection of obstructive sleep apnea: A review.Sleep Med Rev. 2018 Oct;41:149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Sleep Med Rev. 2018. PMID: 30149930 Review.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea devices for out-of-center (OOC) testing: technology evaluation.J Clin Sleep Med. 2011 Oct 15;7(5):531-48. doi: 10.5664/JCSM.1328. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011. PMID: 22003351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-Time Detection of Sleep Apnea Based on Breathing Sounds and Prediction Reinforcement Using Home Noises: Algorithm Development and Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Feb 22;25:e44818. doi: 10.2196/44818. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36811943 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of obstructive sleep apnea in more than 8000 subjects using frequency optimized orthogonal wavelet filter bank with respiratory and oximetry signals.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105364. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105364. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35299046
Cited by
-
Association between pollinosis and obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome in the US population: evidence from the NHANES database 2005-2018.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Mar 13;25(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03581-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40082843 Free PMC article.
-
ReSTech project on Xiaomi wearable devices for monitoring and detecting obstructive sleep apnoea: observational study protocol.BMJ Open. 2025 Aug 13;15(8):e101824. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-101824. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40812810 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of sleep apnea using smartphone-embedded inertial measurement unit.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99801-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295732 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Automated Sleep Study.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Jun;52(6):1463-1491. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03486-0. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38493234 Review.
-
SiCRNN: A Siamese Approach for Sleep Apnea Identification via Tracheal Microphone Signals.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 5;24(23):7782. doi: 10.3390/s24237782. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapur V.K., Auckley D.H., Chowdhuri S., Kuhlmann D.C., Mehra R., Ramar K., Harrod C.G. Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: An American academy of sleep medicine clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2017;13:479–504. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6506. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) [(accessed on 7 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/sleep-apnea/sleep-apnea-ahi-numbers.
-
- Ronquidos y Apnea, Trastornos del Sueño Más Comunes en México. 2020. [(accessed on 30 September 2023)]. Available online: https://www.dgcs.unam.mx/boletin/bdboletin/2020_226.html.
-
- de Salud S. En México, Cuatro por Ciento de Hombres y dos por Ciento de Mujeres Sufren Apnea del Sueño.gob.mx. 2016. [(accessed on 30 September 2023)]. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/salud/articulos/en-mexico-cuatro-por-ciento-de-hombres....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical