Tacrolimus as a Promising Drug for Epistaxis and Gastrointestinal Bleeding in HHT
- PMID: 38068462
- PMCID: PMC10706934
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12237410
Tacrolimus as a Promising Drug for Epistaxis and Gastrointestinal Bleeding in HHT
Abstract
Background: Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a vascular autosomically inherited rare disease. Epistaxis (nose bleeds) is the most common symptom in HHT, leading to anemia and affecting the patient's quality of life. In addition to epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding (GI), more often at older ages, may lead to severe anemia and the need for blood transfusions. Thus, finding drugs to control both types of bleeding is a primary necessity in HHT.
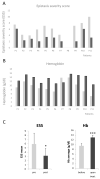
Methods: A cross-sectional observational study was conducted in a series of 11 HHT patients treated with low tacrolimus doses (0.5-2 mg/day) on an off-label prescription basis. Patients showed refractory bleeding to previous treatments. The epistaxis severity score (ESS) and hemoglobin levels were the parameters used to evaluate the impact of tacrolimus. The occurrence of side effects was also recorded.
Results: Tacrolimus was well tolerated in all of the patients except 2 (who stopped the treatment). The remaining patients tolerated the treatment, with a general improvement in their health condition. Epistaxis was significantly reduced when comparing the ESS before and after the treatment. Hemoglobin levels significantly increased, overcoming the anemia, during the course of the treatment.
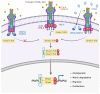
Conclusion: Tacrolimus at low doses should be considered as a promising treatment for epistaxis and gastrointestinal bleeding in HHT.
Keywords: ESS; GI bleeding; HHT; bleeding; epistaxis; hemoglobin; tacrolimus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integration of clinical parameters, genotype and epistaxis severity score to guide treatment for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia associated bleeding.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Jul 13;15(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01453-1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 32660636 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Tacrolimus as Treatment for Bleeding Caused by Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: An Open-Label, Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 7;11(18):5280. doi: 10.3390/jcm11185280. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36142926 Free PMC article.
-
Pazopanib for severe bleeding and transfusion-dependent anemia in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Angiogenesis. 2022 Feb;25(1):87-97. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09807-4. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Angiogenesis. 2022. PMID: 34292451 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Nosebleed (Epistaxis) Executive Summary.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(1):8-25. doi: 10.1177/0194599819889955. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31910122 Review.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia.Ochsner J. 2017 Summer;17(2):157-161. Ochsner J. 2017. PMID: 28638289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025 Jan 9;11(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00585-z. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025. PMID: 39788978 Review.
-
Potential and emerging therapeutics for HHT.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2024 Dec 6;2024(1):724-727. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2024000675. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2024. PMID: 39644056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shovlin C.L., Guttmacher A.E., Buscarini E., Faughnan M.E., Hyland R.H., Westermann C.J.J., Kjeldsen A.D., Plauchu H. Diagnostic criteria for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (RenduOsler-Weber Syndrome) Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;91:66–67. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000306)91:1<66::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jessurun G.A.J., Kamphuis D.J., Van der Zande F.H.R., Nossent J.C. Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in the Netherlands Antilles. High prevalence of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia-related single and multiple cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1993;95:193–198. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(93)90123-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

