PEGylation of Terminal Ligands as a Route to Decrease the Toxicity of Radiocontrast Re6-Clusters
- PMID: 38068892
- PMCID: PMC10706756
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242316569
PEGylation of Terminal Ligands as a Route to Decrease the Toxicity of Radiocontrast Re6-Clusters
Abstract
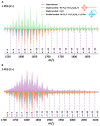
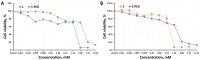
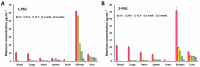
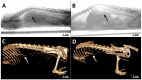
The development of novel radiocontrast agents, mainly used for the visualization of blood vessels, is still an emerging task due to the variety of side effects of conventional X-ray contrast media. Recently, we have shown that octahedral chalcogenide rhenium clusters with phosphine ligands-Na2H14[{Re6Q8}(P(C2H4COO)3)6] (Q = S, Se)-can be considered as promising X-ray contrast agents if their relatively high toxicity related to the high charge of the complexes can be overcome. To address this issue, we propose one of the most widely used methods for tuning the properties of proteins and peptides-PEGylation (PEG is polyethylene glycol). The reaction between the clusters and PEG-400 was carried out in acidic aqueous media and resulted in the binding of up to five carboxylate groups with PEG. The study of cytotoxicity against Hep-2 cells and acute toxicity in mice showed a twofold reduction in toxicity after PEGylation, demonstrating the success of the strategy chosen. Finally, the compound obtained has been used for the visualization of blood vessels of laboratory rats by angiography and computed tomography.
Keywords: PEGylation; X-ray contrast media; acute toxicity; angiography; computed tomography; cytotoxicity; octahedral chalcogenide rhenium cluster; phosphine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Röentgen W.C. On a New Kind of Rays. Phys. Med. Ges. Wurzburg. 1895;137:132–141.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

