Toward Digital Twin Technology for Precision Pharmacology
- PMID: 38069976
- PMCID: PMC12049087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacep.2023.10.024
Toward Digital Twin Technology for Precision Pharmacology
Abstract
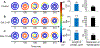
The authors demonstrate the feasibility of technological innovation for personalized medicine in the context of drug-induced arrhythmia. The authors use atomistic-scale structural models to predict rates of drug interaction with ion channels and make predictions of their effects in digital twins of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac myocytes. The authors construct a simplified multilayer, 1-dimensional ring model with sufficient path length to enable the prediction of arrhythmogenic dispersion of repolarization. Finally, the authors validate the computational pipeline prediction of drug effects with data and quantify drug-induced propensity to repolarization abnormalities in cardiac tissue. The technology is high throughput, computationally efficient, and low cost toward personalized pharmacologic prediction.
Keywords: digital twins; dofetilide; hERG; iPSC-CMs; moxifloxacin.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures This work was supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants R01HL128537 (to Drs Clancy, Santana, and Vorobyov), R01HL152681 (to Drs Santana and Clancy) and U01HL126273 (to Drs Clancy and Yarov-Yarovy), NIH Common Fund Grant OT2OD026580 (to Drs Clancy and Santana), American Heart Association Career Development Award 19CDA34770101 and Oracle for Research fellowship (to Dr Vorobyov). All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
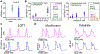

Comment in
-
Building A Pipeline for Precision Antiarrhythmic Therapy.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2024 Feb;10(2):365-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2023.11.016. Epub 2024 Jan 3. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38180434 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kattman SJ, Koonce CH, Swanson BJ, Anson BD. Stem cells and their derivatives: a renaissance in cardiovascular translational research. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2011;4:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Fujifilm. Culturing and assaying calcium transients of 3D cardiac tri-culture microtissues. Retrieved. Accessed November 2, 2023. https://www.fujifilmcdi.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/FCDI_iCell-CMC...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

