Combined cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic and cytokine profiling in tuberculosis meningitis reveals robust and prolonged changes in immunometabolic networks
- PMID: 38070353
- PMCID: PMC10842779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2023.102462
Combined cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic and cytokine profiling in tuberculosis meningitis reveals robust and prolonged changes in immunometabolic networks
Abstract
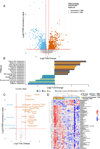
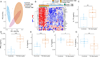
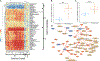
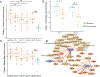
Much of the high mortality in tuberculosis meningitis (TBM) is attributable to excessive inflammation, making it imperative to identify targets for host-directed therapies that reduce pathologic inflammation and mortality. In this study, we investigate how cytokines and metabolites in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) associate with TBM at diagnosis and during TBM treatment. At diagnosis, TBM patients (n = 17) demonstrate significant increases of cytokines and chemokines that promote inflammation and cell migration including IL-17A, IL-2, TNFα, IFNγ, and IL-1β versus asymptomatic controls without known central nervous system pathology (n = 20). Inflammatory immune signaling had a strong positive correlation with immunomodulatory metabolites including kynurenine, lactic acid, and carnitine and strong negative correlations with tryptophan and itaconate. Inflammatory immunometabolic networks were only partially reversed with two months of effective TBM treatment and remained significantly different compared to CSF from controls. Together, these data highlight a critical role for host metabolism in regulating the inflammatory response to TBM and indicate the timeline for restoration of immune homeostasis in the CSF is prolonged.
Keywords: CSF; Cytokines; Meningitis; Metabolomics; Tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
Combined cerebrospinal fluid metabolomic and cytokine profiling in tuberculosis meningitis reveals robust and prolonged changes in immunometabolic networks.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 29:2023.06.26.23291676. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.26.23291676. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024 Jan;144:102462. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2023.102462. PMID: 37425849 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK, Ranjan P. Predictors of long-term neurological sequelae of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis. Eur J Neurol. 2007;14(1):33–7. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson RJ, Rohlwink U, Misra UK, van Crevel R, Mai NTH, Dooley KE, et al. Tuberculous meningitis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(10):581–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

