Effect of percutaneous cerebral oximetry-guided anaesthetic management on postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: study protocol for a single-centre prospective randomised controlled trial in a tertiary academic hospital in China
- PMID: 38070897
- PMCID: PMC10729170
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076419
Effect of percutaneous cerebral oximetry-guided anaesthetic management on postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: study protocol for a single-centre prospective randomised controlled trial in a tertiary academic hospital in China
Abstract
Introduction: Postoperative delirium is a prominent and clinically important complication in older adults after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, resulting in prolonged hospital stay, long-term cognitive impairment and increased morbidity and mortality. Many studies have shown that cerebral desaturation is associated with increased risk of postoperative delirium during on-pump cardiac surgery. However, few studies have focused on the effect of optimising regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) on postoperative delirium during off-pump CABG. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether intraoperative anaesthetic management based on percutaneous cerebral oximetry monitoring decreases the incidence of postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing off-pump CABG.
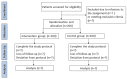
Methods: This single-centre randomised controlled trial will randomly assign 200 patients to the intervention group or the control group at a ratio of 1:1. The patients in the intervention group will be observed by percutaneous cerebral oximetry monitoring that the desaturation (a drop of more than 20% from baseline value or rSO2 less than 55% for >60 consecutive seconds at either probe) during the procedure triggered the intervention strategies, while the cerebral oximetry data of the control group will be hidden from the clinical team and patients will be anaesthetised by the usual anaesthetic management. The primary outcome will be the incidence of postoperative delirium during the first 7 days after off-pump CABG. Delirium will be comprehensively evaluated by the combination of the Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale and the Confusion Assessment Method for the intensive care unit. The secondary outcomes will include the incidence of postoperative acute kidney injury and myocardial infarction during the hospital stay, as well as the intensive care unit and hospital length of stay.
Ethics and dissemination: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Fuwai Hospital (No 2022-1824). Written informed consent will be obtained from each patient or their legal representatives before enrolment. The results of this trial will be published in an international peer-reviewed scientific journal.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2300068537.
Keywords: aged; anaesthesia in cardiology; delirium & cognitive disorders; health services for the aged.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
The relationship between intraoperative cerebral oximetry and postoperative delirium in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a retrospective study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 Nov 14;20(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01180-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 33189145 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological outcome after minimal invasive coronary artery surgery (NOMICS): protocol for an observational prospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 6;7(10):e017823. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017823. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28988183 Free PMC article.
-
Care guided by tissue oxygenation and haemodynamic monitoring in off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (Bottomline-CS): assessor blind, single centre, randomised controlled trial.BMJ. 2025 Mar 24;388:e082104. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2024-082104. BMJ. 2025. PMID: 40127893 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Intraoperative Cerebral Oximetry Monitoring on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and ICU Stay in Adult Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 1;8:814313. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.814313. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35178431 Free PMC article.
-
Does off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery have a beneficial effect on long-term mortality and morbidity compared with on-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014 Jul;19(1):149-59. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu075. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24659552 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for postoperative delirium in patients with off‑pump coronary artery bypass grafting.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Jun 30;16(6):3944-3955. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-578. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38983165 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Mean Arterial Pressure during Cardiopulmonary Bypass on Postoperative Outcomes in Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2024 Apr;19(2):96-101. doi: 10.18502/jthc.v19i2.16198. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2024. PMID: 40322759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Geriatrics Society Expert Panel on Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults . Postoperative delirium in older adults: best practice statement from the American Geriatrics society. J Am Coll Surg 2015;220:136–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical