The NERP-4-SNAT2 axis regulates pancreatic β-cell maintenance and function
- PMID: 38071217
- PMCID: PMC10710447
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43976-8
The NERP-4-SNAT2 axis regulates pancreatic β-cell maintenance and function
Abstract
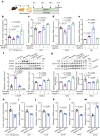
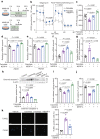
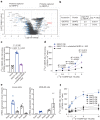
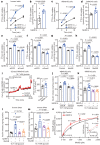
Insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells is regulated by multiple stimuli, including nutrients, hormones, neuronal inputs, and local signalling. Amino acids modulate insulin secretion via amino acid transporters expressed on β cells. The granin protein VGF has dual roles in β cells: regulating secretory granule formation and functioning as a multiple peptide precursor. A VGF-derived peptide, neuroendocrine regulatory peptide-4 (NERP-4), increases Ca2+ influx in the pancreata of transgenic mice expressing apoaequorin, a Ca2+-induced bioluminescent protein complex. NERP-4 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from isolated human and mouse islets and β-cell-derived MIN6-K8 cells. NERP-4 administration reverses the impairment of β-cell maintenance and function in db/db mice by enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing metabolic stress. NERP-4 acts on sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 2 (SNAT2), thereby increasing glutamine, alanine, and proline uptake into β cells and stimulating insulin secretion. SNAT2 deletion and inhibition abolish the protective effects of NERP-4 on β-cell maintenance. These findings demonstrate a novel autocrine mechanism of β-cell maintenance and function that is mediated by the peptide-amino acid transporter axis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Gutiérrez-Preciado A, Romero H, Peimbert M. An evolutionary perspective on amino acids. Nat. Educ. 2010;3:29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

