Lisocabtagene Maraleucel in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Primary Analysis of the Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cohort From TRANSCEND NHL 001, a Phase I Multicenter Seamless Design Study
- PMID: 38072625
- PMCID: PMC11741176
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02214
Lisocabtagene Maraleucel in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Primary Analysis of the Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cohort From TRANSCEND NHL 001, a Phase I Multicenter Seamless Design Study
Abstract
Purpose: To report the primary analysis results from the mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cohort of the phase I seamless design TRANSCEND NHL 001 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02631044) study.
Methods: Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL after ≥two lines of previous therapy, including a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), an alkylating agent, and a CD20-targeted agent, received lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) at a target dose level (DL) of 50 × 106 (DL1) or 100 × 106 (DL2) chimeric antigen receptor-positive T cells. Primary end points were adverse events (AEs), dose-limiting toxicities, and objective response rate (ORR) by independent review committee per Lugano criteria.
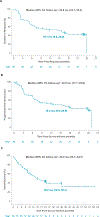
Results: Of 104 leukapheresed patients, liso-cel was infused into 88. Median (range) number of previous lines of therapy was three (1-11) with 30% receiving ≥five previous lines of therapy, 73% of patients were age 65 years and older, 69% had refractory disease, 53% had BTKi refractory disease, 23% had TP53 mutation, and 8% had secondary CNS lymphoma. Median (range) on-study follow-up was 16.1 months (0.4-60.5). In the efficacy set (n = 83; DL1 + DL2), ORR was 83.1% (95% CI, 73.3 to 90.5) and complete response (CR) rate was 72.3% (95% CI, 61.4 to 81.6). Median duration of response was 15.7 months (95% CI, 6.2 to 24.0) and progression-free survival was 15.3 months (95% CI, 6.6 to 24.9). Most common grade ≥3 treatment-emergent AEs were neutropenia (56%), anemia (37.5%), and thrombocytopenia (25%). Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) was reported in 61% of patients (grade 3/4, 1%; grade 5, 0), neurologic events (NEs) in 31% (grade 3/4, 9%; grade 5, 0), grade ≥3 infections in 15%, and prolonged cytopenia in 40%.
Conclusion: Liso-cel demonstrated high CR rate and deep, durable responses with low incidence of grade ≥3 CRS, NE, and infections in patients with heavily pretreated R/R MCL, including those with high-risk, aggressive disease.
Figures


References
-
- Martin P, Maddocks K, Leonard JP, et al.: Postibrutinib outcomes in patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 127:1559–63, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Jain P, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Zhang S, et al.: Long-term outcomes and mutation profiling of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who discontinued ibrutinib. Br J Haematol 183:578–587, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Cheah CY, Chihara D, Romaguera JE, et al.: Patients with mantle cell lymphoma failing ibrutinib are unlikely to respond to salvage chemotherapy and have poor outcomes. Ann Oncol 26:1175–1179, 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

