Identification of ITPR1 gene as a novel target for hsa-miR-34b-5p in non-obstructive azoospermia: a Ca2+/apoptosis pathway cross-talk
- PMID: 38072953
- PMCID: PMC10710998
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-49155-5
Identification of ITPR1 gene as a novel target for hsa-miR-34b-5p in non-obstructive azoospermia: a Ca2+/apoptosis pathway cross-talk
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Identification of ITPR1 gene as a novel target for hsa-miR-34b-5p in non-obstructive azoospermia: a Ca2+/apoptosis pathway cross-talk.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 14;14(1):3722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53786-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38355618 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
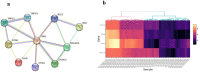
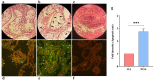
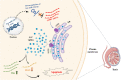
MiR-34b-5p has been reported as a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker for infertility. However, no gene targets regulating the mechanism of cation of this miRNA are known. In this study, using gene set enrichment analysis the Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor Type 1 (ITPR1) gene was identified as the sole target for hsa-miR-34b-5p, and found significantly overexpressed in non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) patients. This finding was confirmed by qRT-PCR on fresh testicular tissues from NOA patients. Then, pathway enrichment analysis as well as the diagnostic value analysis of hsa-miR-34b-5p/ITPR1 indicated ITPR1 as a hub gene in the calcium (Ca2+)-apoptosis pathway, and a valuable predictive biomarker for NOA. Moreover, gene expression and histological assays showed the association of the effects of ITPR1's increased expression on spermatogenesis failure through induction of apoptosis in NOA patients. These data suggested that the hsa-miR-34b-5p/ITPR1 axis could serve as a potential regulatory predictive biomarker for human spermatogenesis through the Ca2+-apoptosis pathway cross-talk.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Maleki B, Shabani S, Vallian Borojeni S. The role of miRNA in spermatogenesis and male infertility. Lab. Diagn. 2018;10:48–55.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

