Orphan peptide and G protein-coupled receptor signalling in alcohol use disorder
- PMID: 38073127
- PMCID: PMC10953447
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.16301
Orphan peptide and G protein-coupled receptor signalling in alcohol use disorder
Abstract
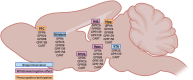
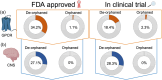
Neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have long been, and continue to be, one of the most popular target classes for drug discovery in CNS disorders, including alcohol use disorder (AUD). Yet, orphaned neuropeptide systems and receptors (oGPCR), which have no known cognate receptor or ligand, remain understudied in drug discovery and development. Orphan neuropeptides and oGPCRs are abundantly expressed within the brain and represent an unprecedented opportunity to address brain function and may hold potential as novel treatments for disease. Here, we describe the current literature regarding orphaned neuropeptides and oGPCRs implicated in AUD. Specifically, in this review, we focus on the orphaned neuropeptide cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART), and several oGPCRs that have been directly implicated in AUD (GPR6, GPR26, GPR88, GPR139, GPR158) and discuss their potential and pitfalls as novel treatments, and progress in identifying their cognate receptors or ligands.
Keywords: CART; GPCR; GPR135; GPR158; GPR26; GPR6; GPR88; alcohol use disorder; neuropeptide; orphan.
© 2023 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Christopoulos, A. , Davenport, A. P. , Kelly, E. , Marrion, N. V. , Peters, J. A. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Sharman, J. L. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , & Collaborators, C. (2017). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18: G protein‐coupled receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(Suppl 1), S17–S129. 10.1111/bph.13878 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Christopoulos, A. , Davenport, A. P. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , Abbracchio, M. P. , Alexander, W. , Al‐Hosaini, K. , Back, M. , Barnes, N. M. , Bathgate, R. , … Ye, R. D. (2021). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2021/22: G protein‐coupled receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 178(Suppl 1), S27–S156. 10.1111/bph.15538 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Fabbro, D. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , Boison, D. , Burns, K. E. , Dessauer, C. , Gertsch, J. , Helsby, N. A. , Izzo, A. A. , Koesling, D. , … Wong, S. S. (2021). THE CONCISE GUIDE TO PHARMACOLOGY 2021/22: Enzymes. British Journal of Pharmacology, 178(S1), S313–S411. 10.1111/bph.15542 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Southan, C. , Buneman, O. P. , Cidlowski, J. A. , Christopoulos, A. , Davenport, A. P. , Fabbro, D. , Spedding, M. , Striessnig, J. , Davies, J. A. , Ahlers‐Dannen, K. E. , … Zolghadri, Y. (2021). THE CONCISE GUIDE TO PHARMACOLOGY 2021/22: Other Protein Targets. British Journal of Pharmacology, 178(S1), S1–S26. 10.1111/bph.15537 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

