Enhancement of a recombinase-aided amplification assay using betaine and pullulan
- PMID: 38073880
- PMCID: PMC10699723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2022.06.002
Enhancement of a recombinase-aided amplification assay using betaine and pullulan
Abstract
Background: Nucleic acid amplification enhancers suitable for use in a recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) assay were studied for the first time, and amplification of a long-fragment (509 bp) was initially explored.
Methods: Using recombinant plasmids and clinical samples, RAA fluorescence and basic methods were used to evaluate the efficacy. The fluorescence method was evaluated by threshold time and fluorescence value, and the basic method was characterized by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
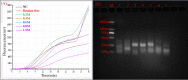
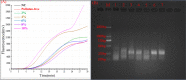
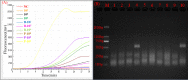
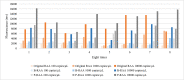
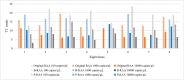
Results: Taking a previously established RAA assay for HPV18 as an example, we demonstrated that the addition of 0.2 M, 0.4 M, and 0.6 M betaine and 10% pullulan could enhance the RAA. The new RAA assays with betaine and pullulan were named B-RAA and P-RAA, respectively. Using the B-RAA and P-RAA fluorescence methods, the threshold time values could be shortened by 1.72-2.32 minutes and 2.60 minutes, respectively, and the fluorescence values could be enhanced by 8847.25-9094.37 mv and 5250 mv, respectively. Using the basic method, the sensitivity could be increased 10-fold. We successfully amplified a long-fragment of 509 bp using a P-RAA assay with a sensitivity of 102 copies/µL (compared with 103 copies/µL in the RAA assay).
Conclusions: Thus, we concluded that betaine and pullulan are effective additives to enhance the sensitivity of RAA assays.
Keywords: Betaine; Long-fragment; Nucleic acid amplification enhancer; Pullulan; RAA.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification-lateral-flow dipstick and real-time fluorescence-based reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification methods for detection of the Newcastle disease virus in chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Jul;99(7):3393-3401. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.03.018. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32616233 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of a fluorescent recombinase-aided isothermal amplification assay for nucleic acid detection of Paraginiumus skrjabini and preliminary evaluation of its detection efficiency].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 26;33(5):464-469. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2021218. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34791843 Chinese.
-
[Establishment and preliminary application of a recombinase-aided isothermal amplification assay-based multiplex nucleic acid assay for detection of three Echinococcus species].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 19;33(4):339-345. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2021094. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34505439 Chinese.
-
[Establishment of a recombinase-aided isothermal amplification assay for nucleic acid detection of Angiostrongylus cantonensis].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 3;32(4):350-354. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020091. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32935507 Chinese.
-
RAP: A Novel Approach to the Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Respiratory Viruses.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 5;9:766411. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.766411. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34805120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and application of a rapid visualization method for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus nucleic acid.Infect Med (Beijing). 2024 Apr 16;3(2):100111. doi: 10.1016/j.imj.2024.100111. eCollection 2024 Jun. Infect Med (Beijing). 2024. PMID: 38948389 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced One-Pot RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Reaction with Glycerol and Betaine for High-Sensitivity Diagnosis of mecA-Carrying Strains in Clinical Samples.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 31;10(5):4599-4606. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09078. eCollection 2025 Feb 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39959114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C, Li XN, Li GX, et al. Use of a rapid reverse-transcription recombinase aided amplification assay for respiratory syncytial virus detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018;90:90–95. - PubMed
-
- Xue GH, Li SL, Zhang WW, et al. Reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid detection of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Anal. Chem. 2020;92:9699–9705. - PubMed
-
- Zhang RQ, Li GX, Li XN, et al. A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay incorporating competitive internal control to detect Bordetella pertussis using the DNA obtained by boiling. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019;86:108–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

