The role of SARS-COV-2 infection in promoting abnormal immune response and sepsis: A comparison between SARS-COV-2-related sepsis and sepsis from other causes
- PMID: 38073889
- PMCID: PMC10699677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2023.04.006
The role of SARS-COV-2 infection in promoting abnormal immune response and sepsis: A comparison between SARS-COV-2-related sepsis and sepsis from other causes
Abstract
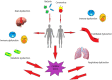
Background: COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus is characterized by respiratory compromise and immune system involvement, even leading to serious disorders, such as cytokine storm.
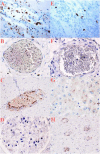
Methods: We then conducted a literature review on the topic of sepsis and covid-19, and in parallel conducted an experimental study on the histological finding of patients who died from SARS-Covid 19 infection and a control group.
Results: Sepsis associated with covid-19 infection has some similarities and differences from that from other causes.
Conclusion: In this paper the complex interplay between the 2 disorders was discussed, focusing on the similarities and on the effect that one could have on the other. A preliminary experimental section that demonstrates the multisystemic involvement in subjects who die from SARS-CoV-2 is also proposed.
Keywords: Cytokine storm; SARS-COV-2; SARS-CoV-2; Sepsis; Septic shock.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Network-Based Analysis Reveals the Mechanism Underlying Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Virus in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 9;11:590459. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.590459. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362771 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Sepsis.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Dec 17;51(SI-1):3301-3311. doi: 10.3906/sag-2108-239. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34590796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hazards of the Cytokine Storm and Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Patients With COVID-19: Review.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Aug 13;22(8):e20193. doi: 10.2196/20193. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32707537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Receptor Activation Patterns Involving TLR and NLR Synergisms in COVID-19, ALI/ARDS and Sepsis Cytokine Storms: A Review and Model Making Novel Predictions and Therapeutic Suggestions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 20;22(4):2108. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042108. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: a promising inhibitory strategy.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Nov-Dec;34(6):1971-1975. doi: 10.23812/20-1-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 33016027
Cited by
-
Virome analysis provides new insights into the pathogenesis mechanism and treatment of SLE disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 24;14:1484529. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1484529. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39512588 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning model for clinical outcome prediction using longitudinal inpatient electronic health records.JAMIA Open. 2025 Apr 10;8(2):ooaf026. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooaf026. eCollection 2025 Apr. JAMIA Open. 2025. PMID: 40213364 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress in Sepsis: A Focus on Cardiac Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 2;25(5):2912. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052912. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474158 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating single-nucleus RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics to elucidate a specialized subpopulation of astrocytes, microglia and vascular cells in brains of mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis-associated encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jul 3;21(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03161-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38961424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czerny M., Gottardi R., Puiu P., et al. Corrigendum to 'Impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the care of patients with acute and chronic aortic conditions'. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021;60(3):724–725. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezab314. Erratum for: Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 May 8;59(5):1096-1102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

