The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the provision of outpatient clinic services in East Jerusalem hospitals: patients' perspectives
- PMID: 38074699
- PMCID: PMC10704241
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1252449
The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the provision of outpatient clinic services in East Jerusalem hospitals: patients' perspectives
Abstract
Background: Due to the decreased availability, accessibility, and quality of services, the COVID-19 pandemic has an impact on the healthcare system. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, patients' perceptions of healthcare have changed, and out-patient visits to clinics have decreased. As part of the COVID-19 outbreak in East Jerusalem, this study aims to assess how patients perceive the way that outpatient clinic services were delivered before and during COVID-19 outbreak.
Methodology: Convenience sampling and self-reported questionnaires were used in a cross-sectional study. Three hundred people from three significant outpatient clinic hospitals in East Jerusalem-Al-Makassed Hospital, Augusta Victoria Hospital, and Sant-Joseph Hospital- made up the sample. Multivariate tests, frequencies, and percentages were used in the statistical analysis.
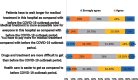
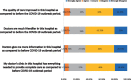
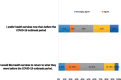
Results: The results showed that the most of the participants (98.6%) had negative opinion when the current situation is compared with before the COVID-19 period in terms of accessibility, availability of resources, quality of care, attitudes and patient's preference. Finally, multivariate analysis indicated a significant relationship between participant opinion and education level and participants with educational levels of 12 study years or less had more positive opinions of the delivery of the healthcare system during the COVID-19 outbreak period than the group with more than 12 study years. Also, the multivariate analysis revealed a significant `relationship between participant opinion and the duration of the illness as those with years of illness and less had more negative opinion toward the delivery of the healthcare system than those with more than 3 years of illness.
Conclusion: This study found that when the current situation during the COVID-19 outbreak is compared to before the COVID-19 period in terms of accessibility, availability of resources, quality of care, attitudes, and patient preferences, the majority of the participants with chronic diseases or cancer had a negative opinion. Policymakers and health managers should enhance patient preferences and attitudes during the COVID-19 pandemic and other pandemics by increasing accessibility, availability of health resources, and the quality of healthcare.
Keywords: East Jerusalem; a patient preferences; accessibility; attitudes; availability of resources; outpatient clinics; quality of care.
Copyright © 2023 Ahmead and Daghlas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
COVID-19 and resilience of healthcare systems in ten countries.Nat Med. 2022 Jun;28(6):1314-1324. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01750-1. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35288697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. (2020). Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a... (Accessed February 1, 2022)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials